3D Print
1.Learn about 3D printing (new applications, related materials, machines, new paper):
3D printing technology is constantly evolving, not only in terms of new areas of application, but also in terms of the materials, machines and technologies that are constantly emerging.
1.1 New applications
I. Healthcare: 3D printing is being used to create personalised prosthetics, customised medical devices and bioprinting (biomaterials to make tissues and organs).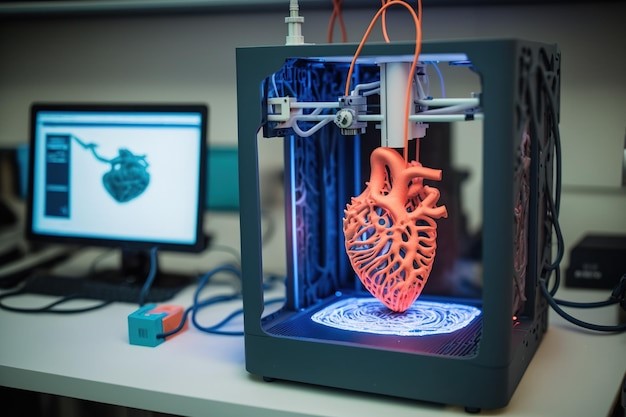
II. Construction: Large-scale 3D printers can build houses and structures, reducing construction time and costs.
III. Aerospace: for the manufacture of lightweight components and prototyping.
IV. Automotive manufacturing: Manufacturing of customised automotive components, including automotive interiors and engine parts.
V. Fashion field: for conceptual clothing design and production.
1.2 New materials
In addition to the original thermoplastic polymerisation materials and photosensitive resins, more and more new materials are now emerging.
I. metal materials: new metal 3D printing materials, such as titanium alloys and aluminium alloys, continue to emerge for the manufacture of strong, corrosion-resistant parts.
II. Biomaterials: Materials used for bioprinting, such as bioink, are used to make human tissues and organs.
III. Ceramics and glass: gradually being used to print ceramic and glass products, such as tableware and decorative items.
IV. Sustainable materials: including biodegradable plastics, recycled plastics, etc., for environmentally friendly and sustainable manufacturing.
1.3 New machines
I. Multi-material printing: A single machine can print with multiple materials at the same time, expanding the range of applications and design possibilities.
II. Larger sized printers: printers for large-scale projects such as construction continue to evolve and are able to print larger sized structures.
III. Increased speed and accuracy: new printing technologies and machines have increased print speed and print accuracy, making them more suitable for a wide range of needs.
IV. Automation and Intelligence: Increased automation, including intelligent design software, automated material change and printing process monitoring.
1.4 New paper
A number of studies are currently exploring the use of paper or similar materials for novel printing techniques.
I. 3D printing with paper models:
Some people will use specific types of paper (e.g., thick cardboard or specially textured paper) to create the shell or external structure of a 3D printed model. These papers will have a specific shape pattern or structure printed onto them by 3D printing technology, and then these papers will be combined to form a 3D object.
II. 3D printing support structures:
In some 3D printing techniques, paper is used as part of the support structure. These papers may be removed after the printing is complete and serve to support the printed object, especially for some complex structures.
III. paper substrates in flexible electronics:
Some research has looked at using paper or similar paper substrates on which flexible electronic components can be printed by certain techniques such as inkjet printing or other similar methods. These flexible electronic components can be used in flexible displays, sensors, and other areas.
2.Our 3D printing project
2.1 Finished product effect display
Using 3D printing to print small models of conchs for large jobs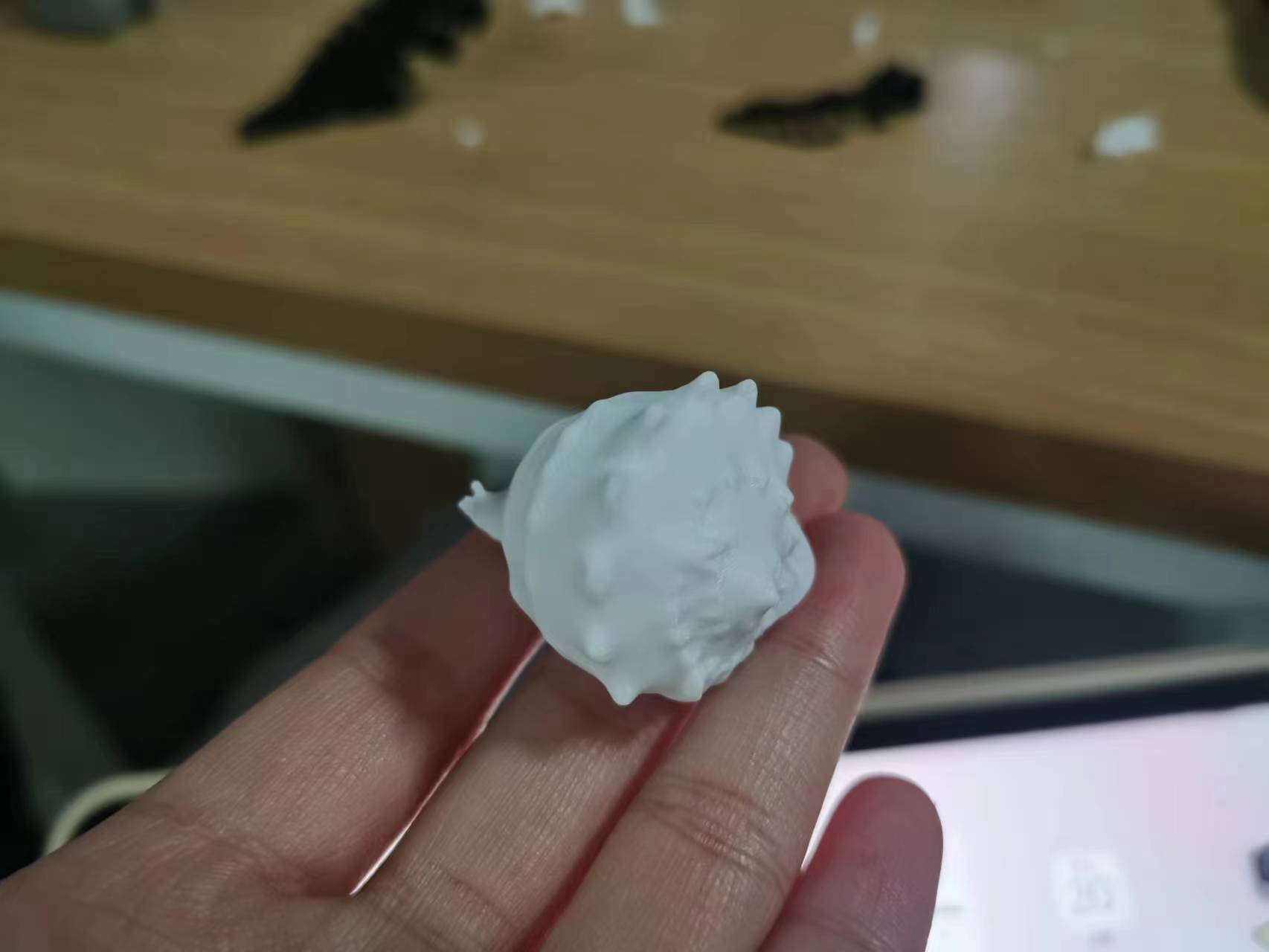
Printing Movable Models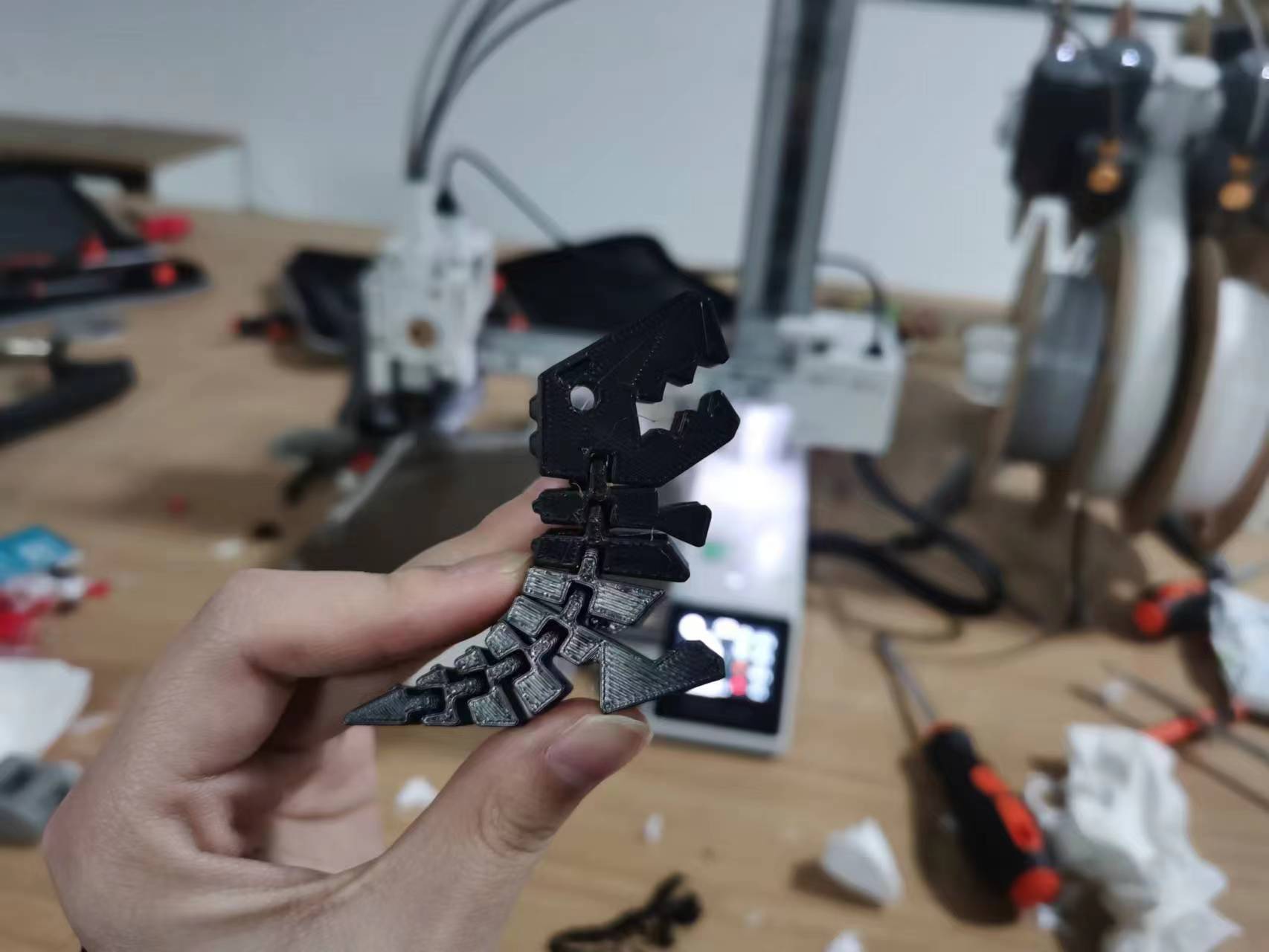
Printable Models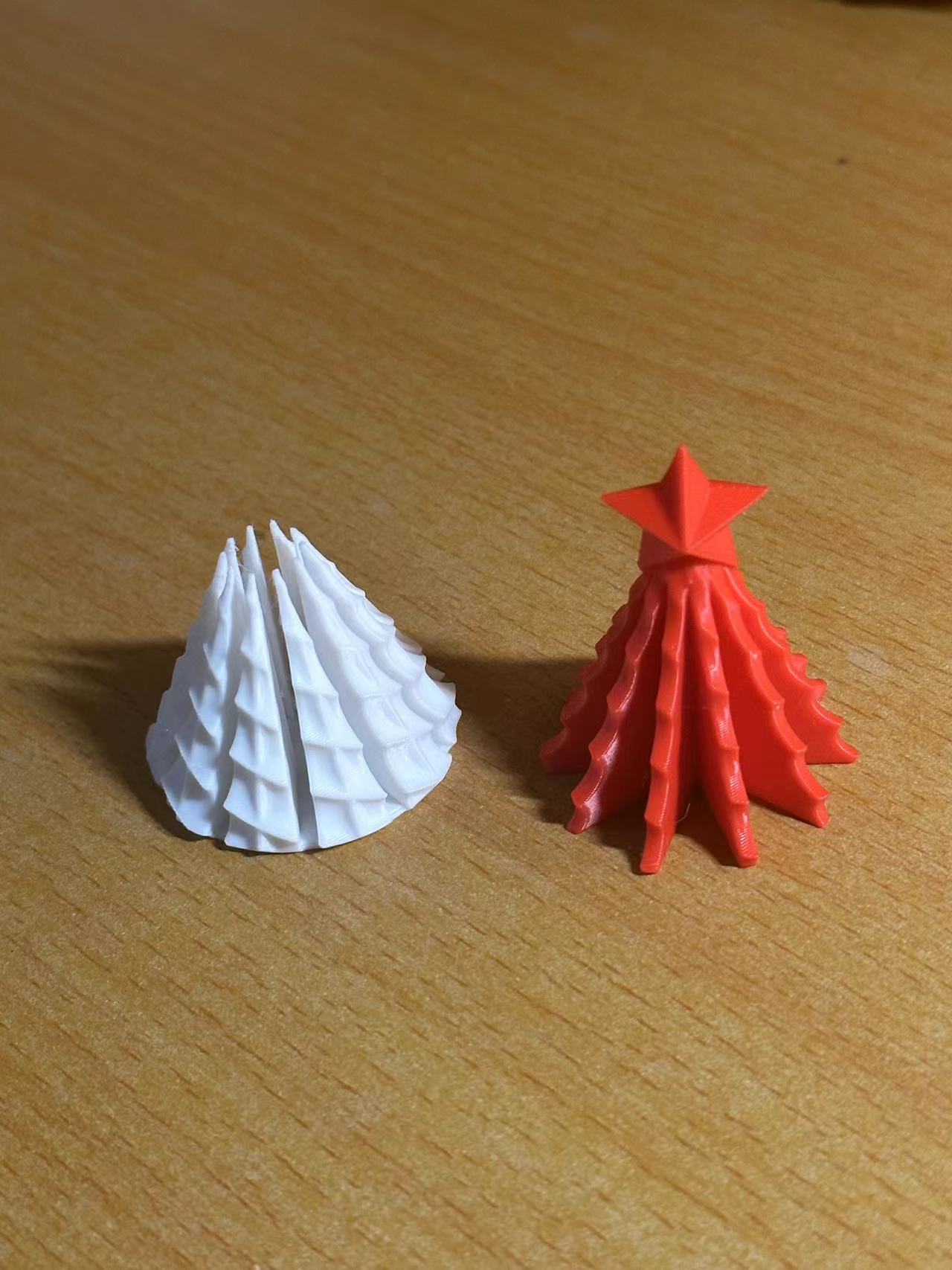
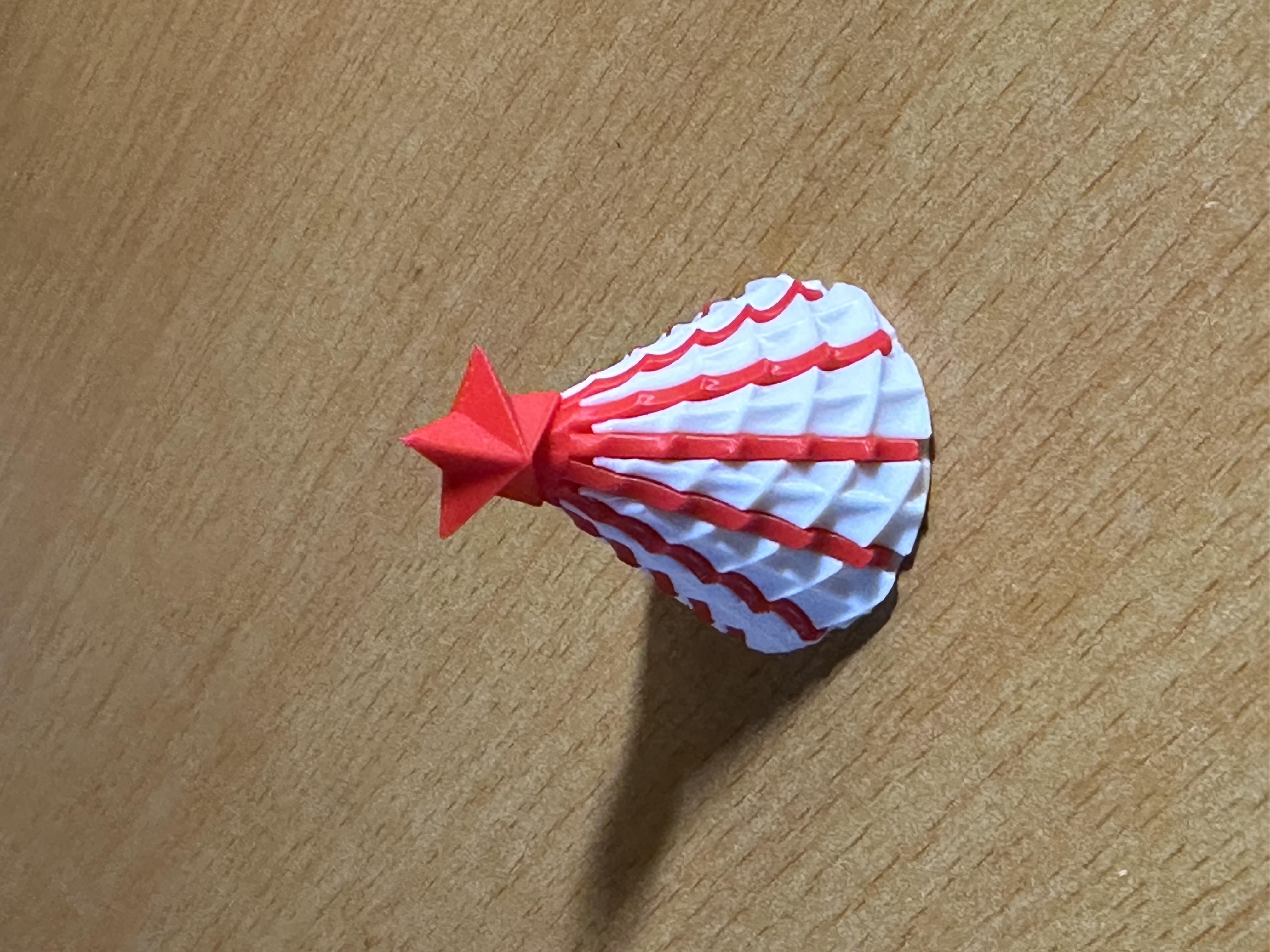

2.2 3D Printing Process Demonstration
Step 1: Prepare Bambu Studio
Download the Bambu Studio software from the website.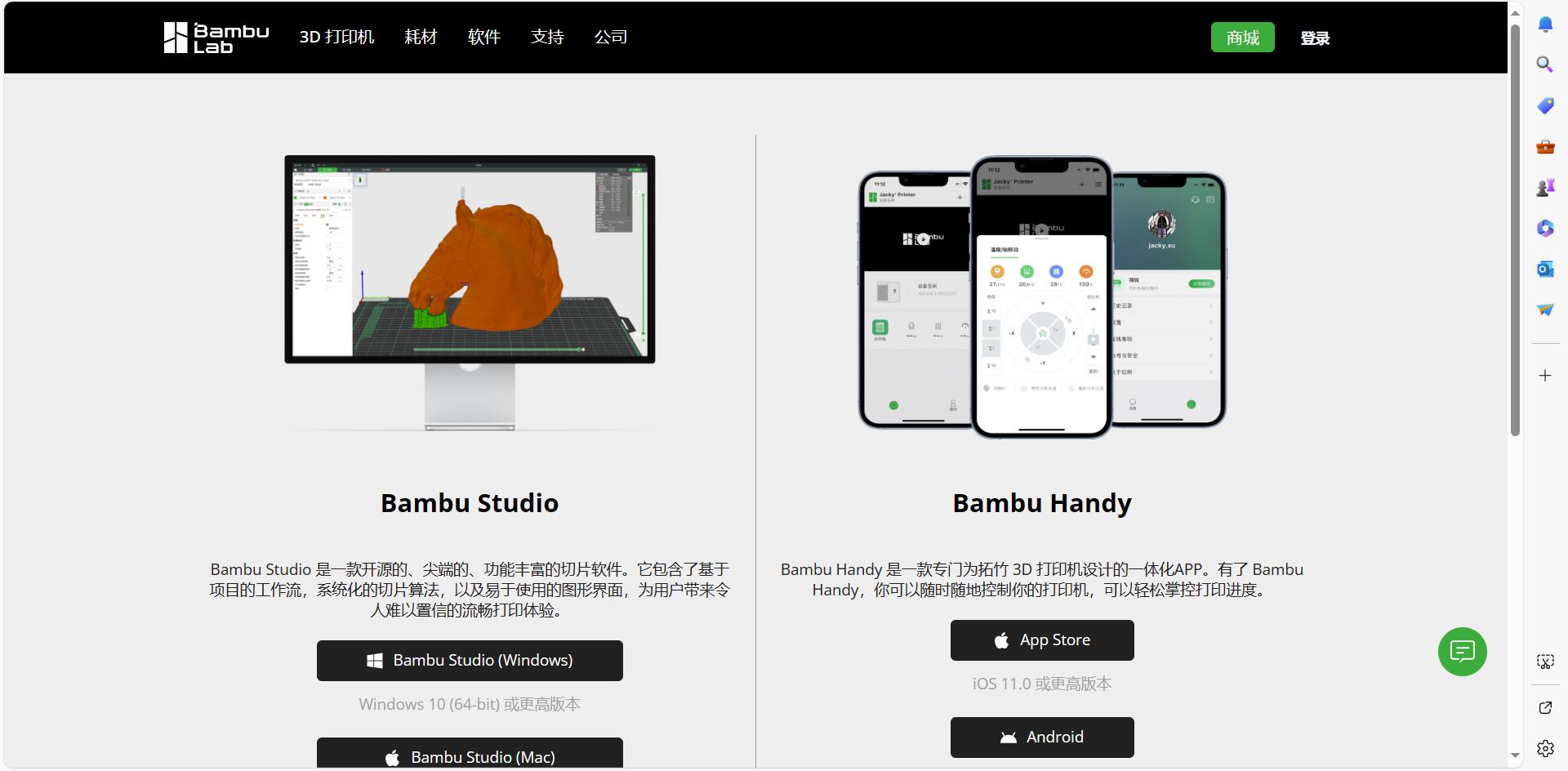
Step 2: Prepare models
Prepare to print three types of models: 1. related to big jobs; 2. movable; 3. Assemblable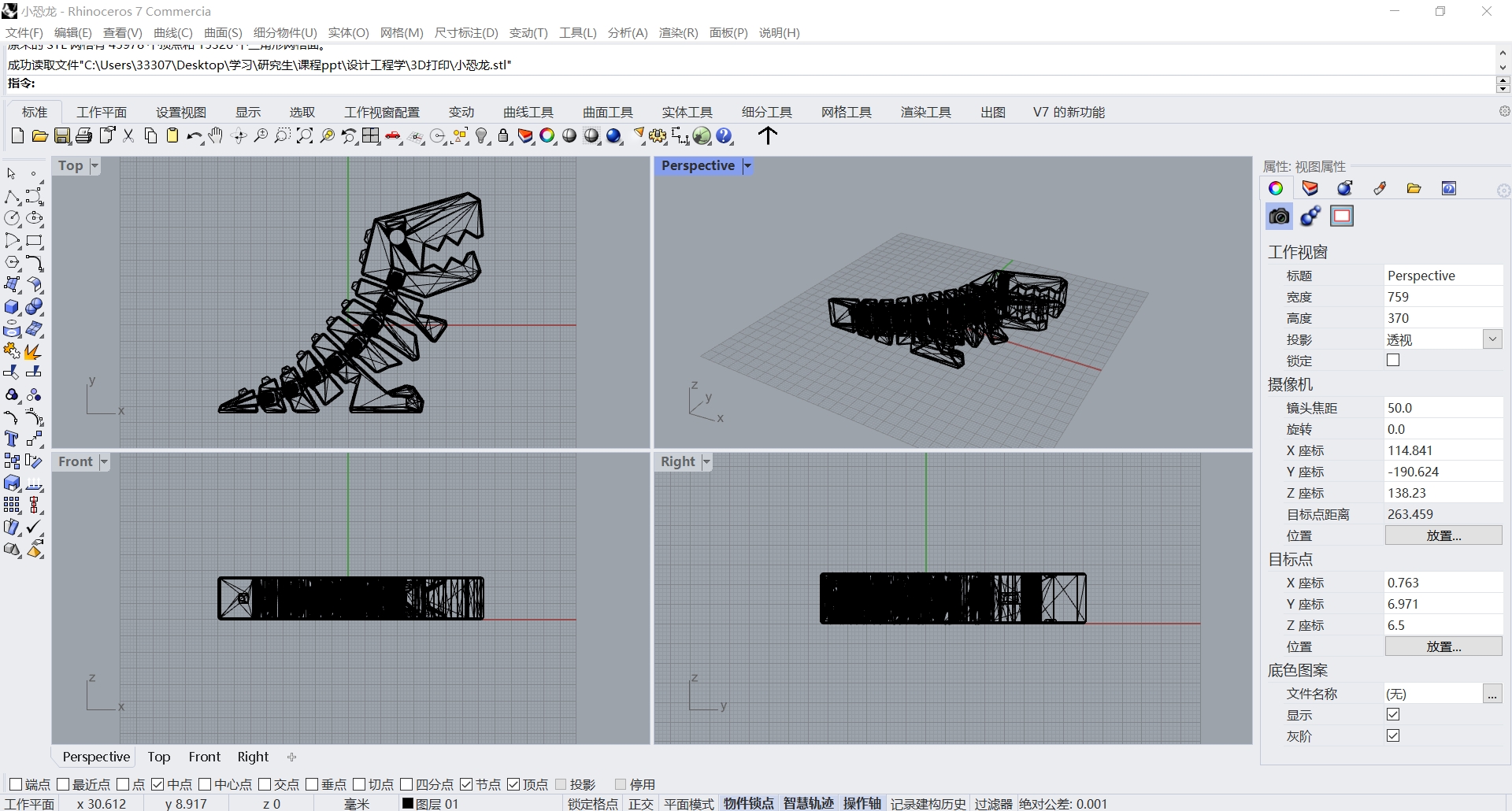
Step 3: Open in Bambu Studio and adjust parameters with slicing software
Model I: Conch model related to large operations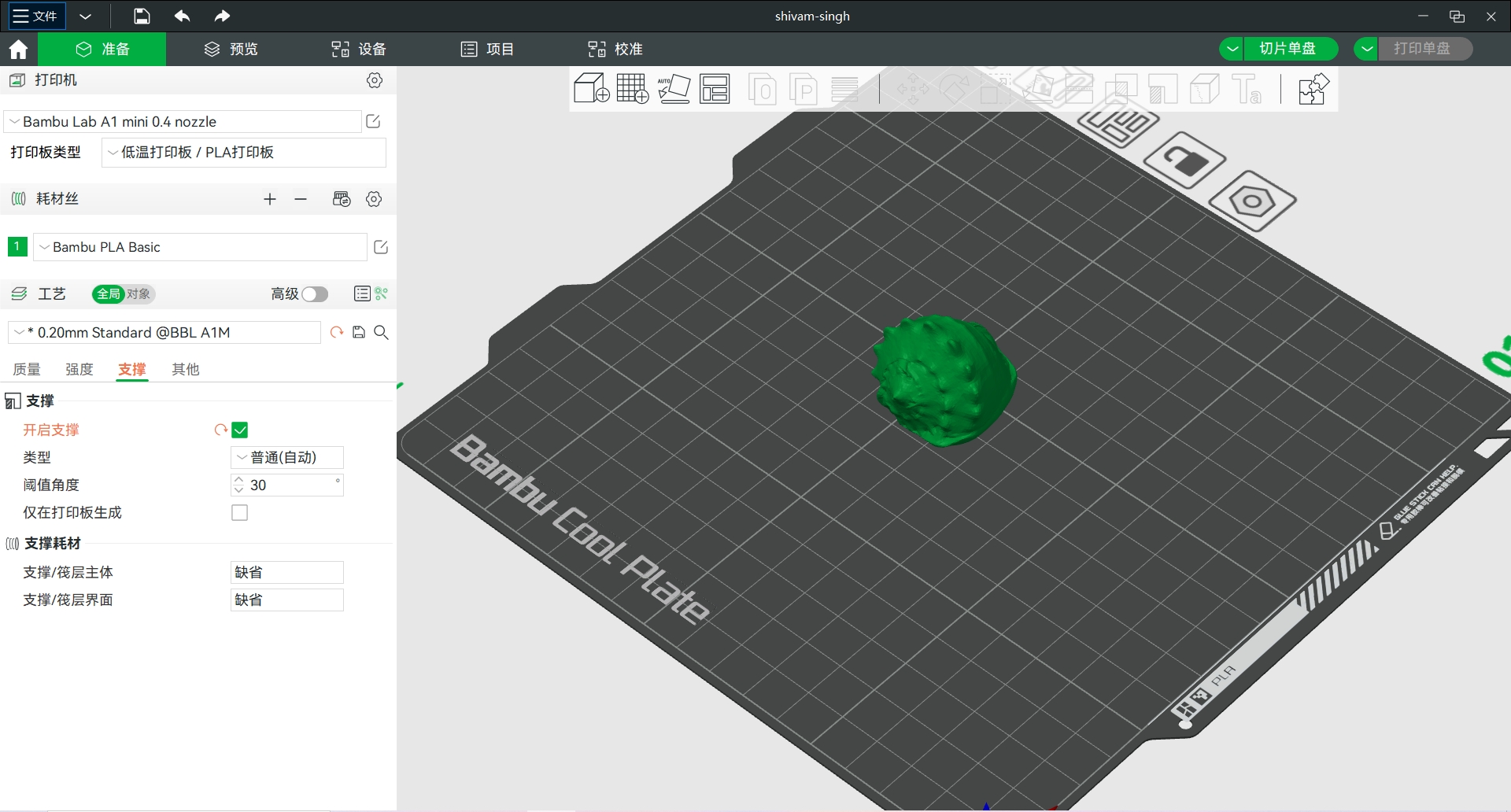
Model 2: movable small dinosaur model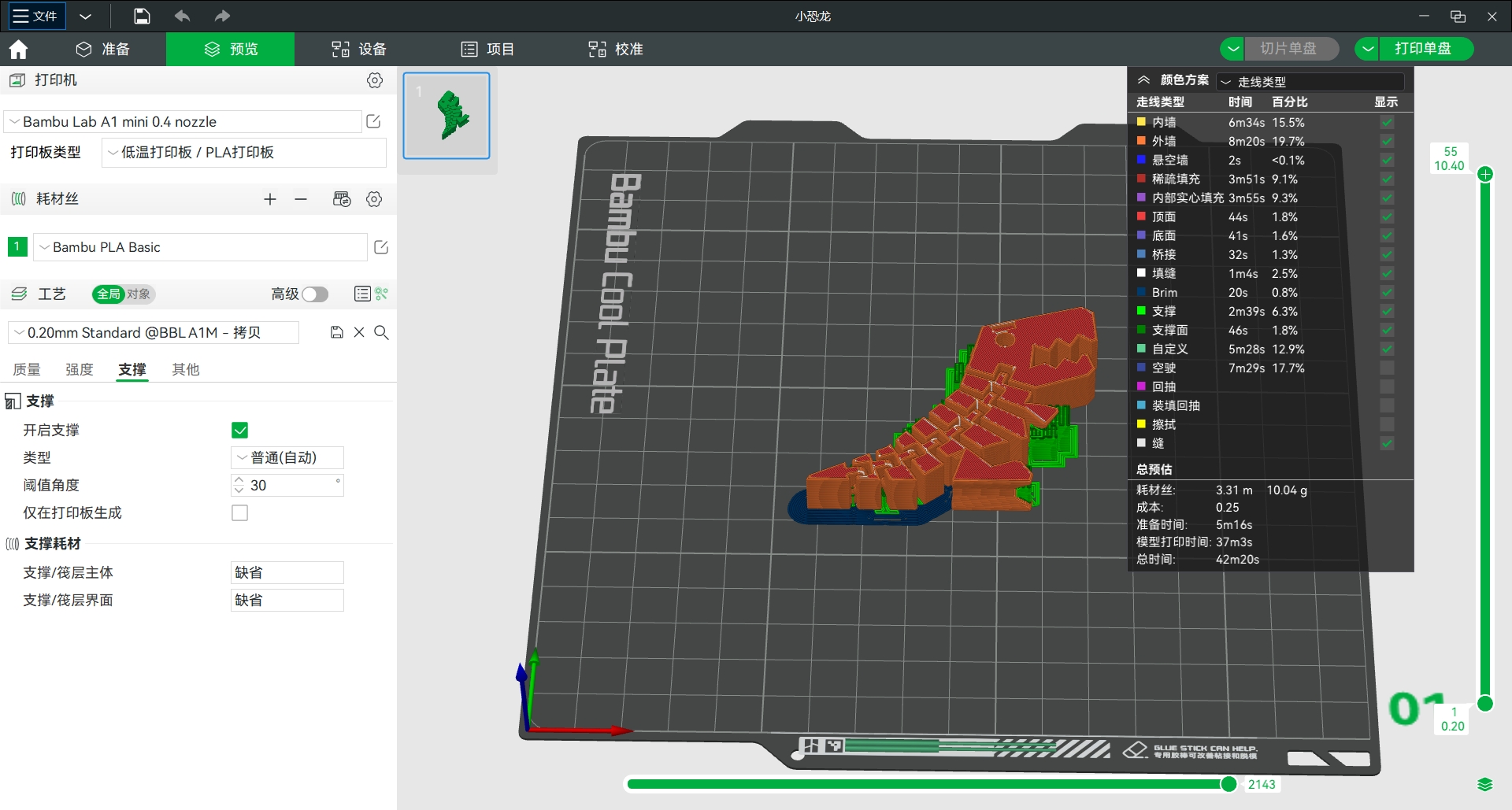
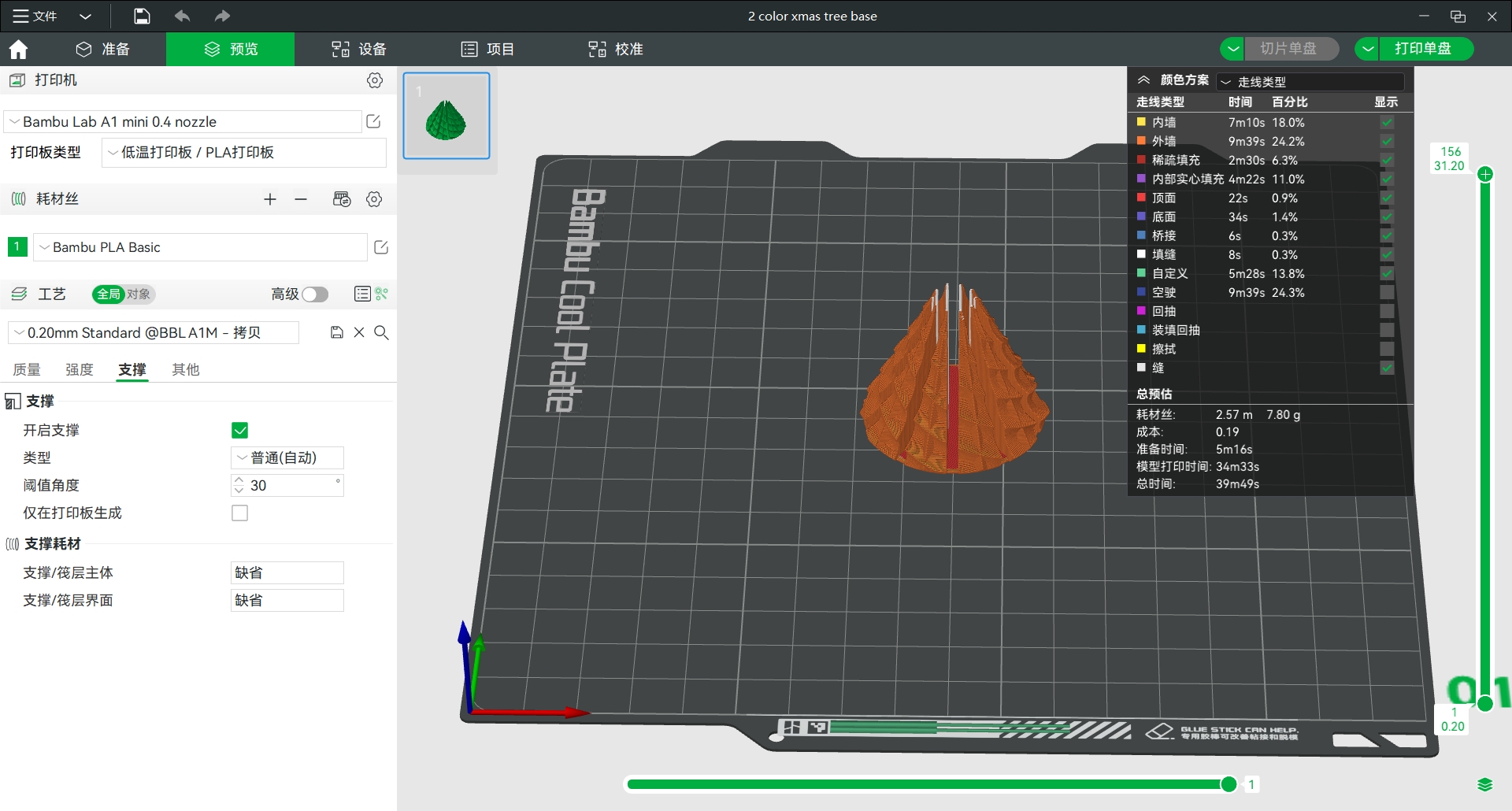
Model 3: assemblable Christmas tree model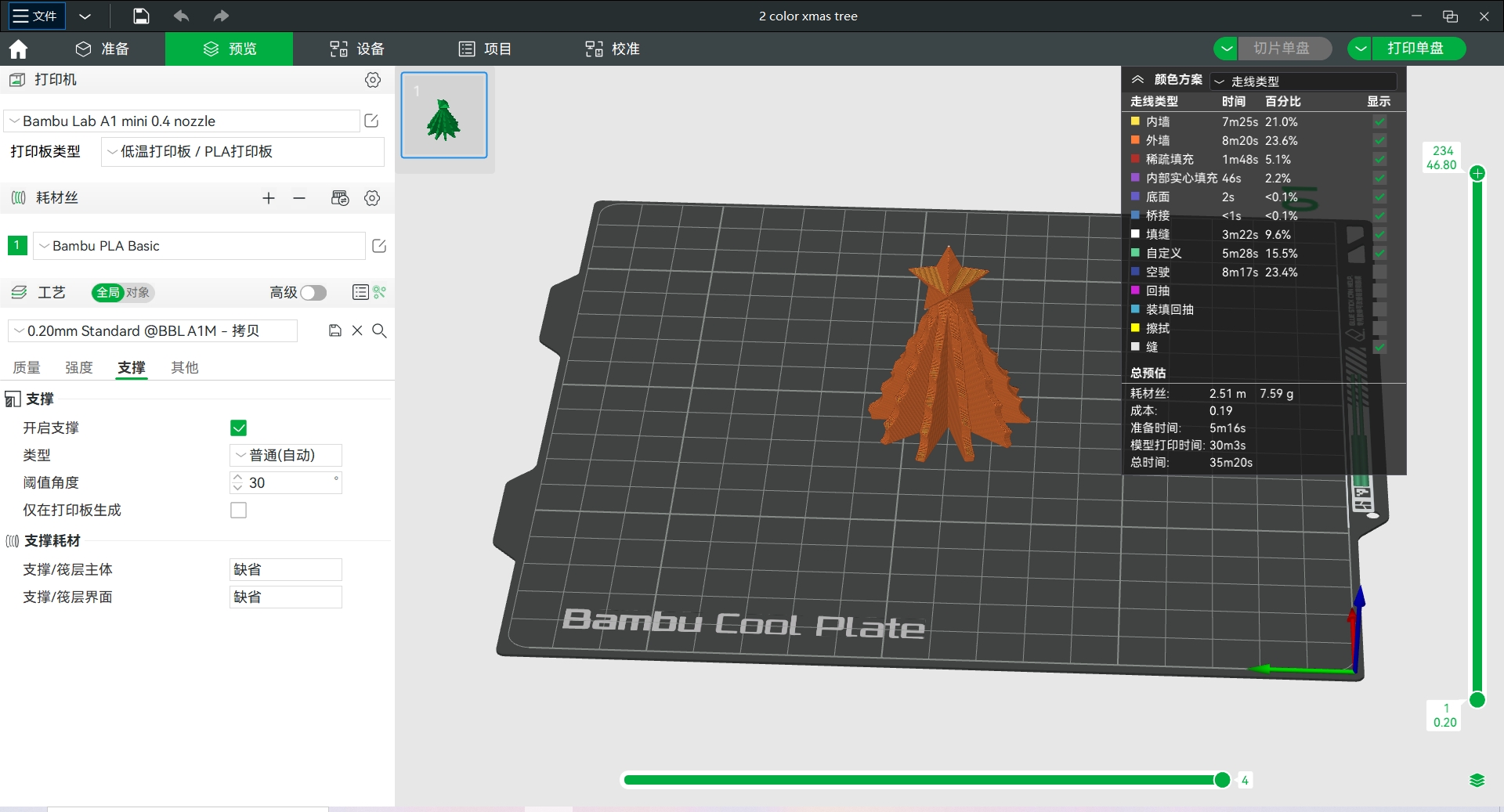
Step 4: Use 3D printer to manufacture it
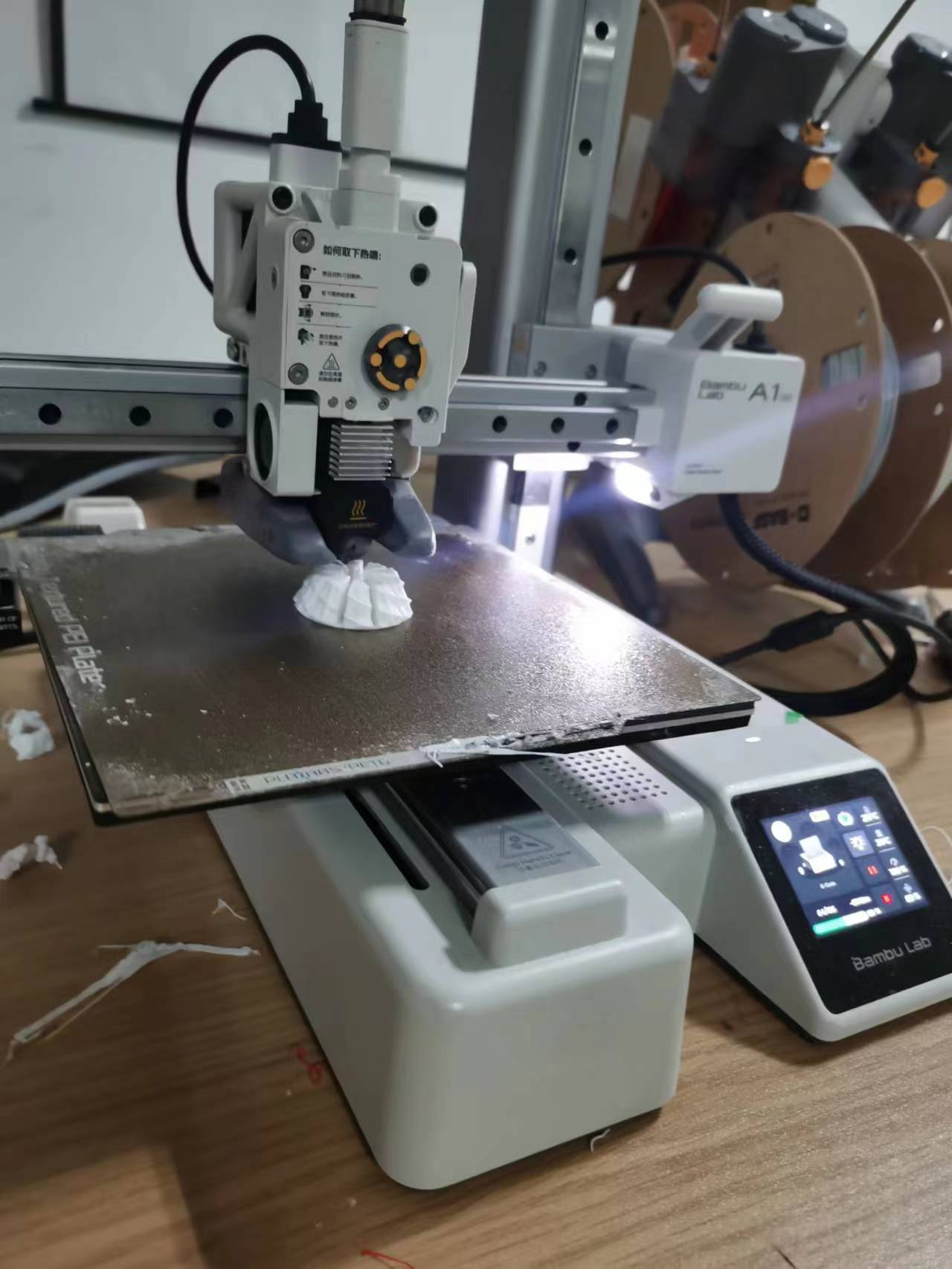

Step 5: Sanding the model
Since models 1 and 3 do not have any obvious supports to deal with, the sanding process for model 2 is shown again.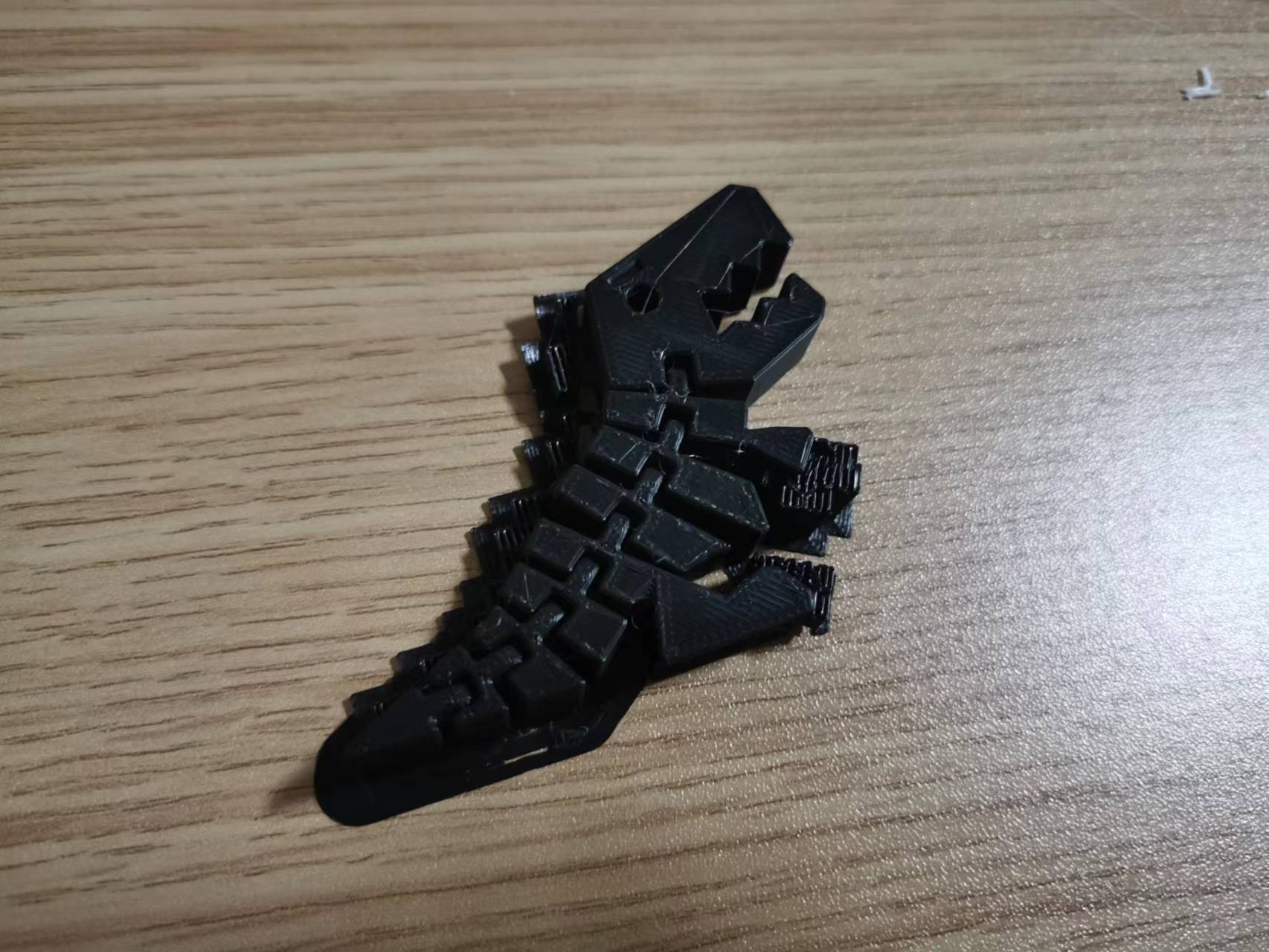
As you can see, since some of the parts in the middle of the movable model are overhanging, the bottom of the model above has some support to deal with.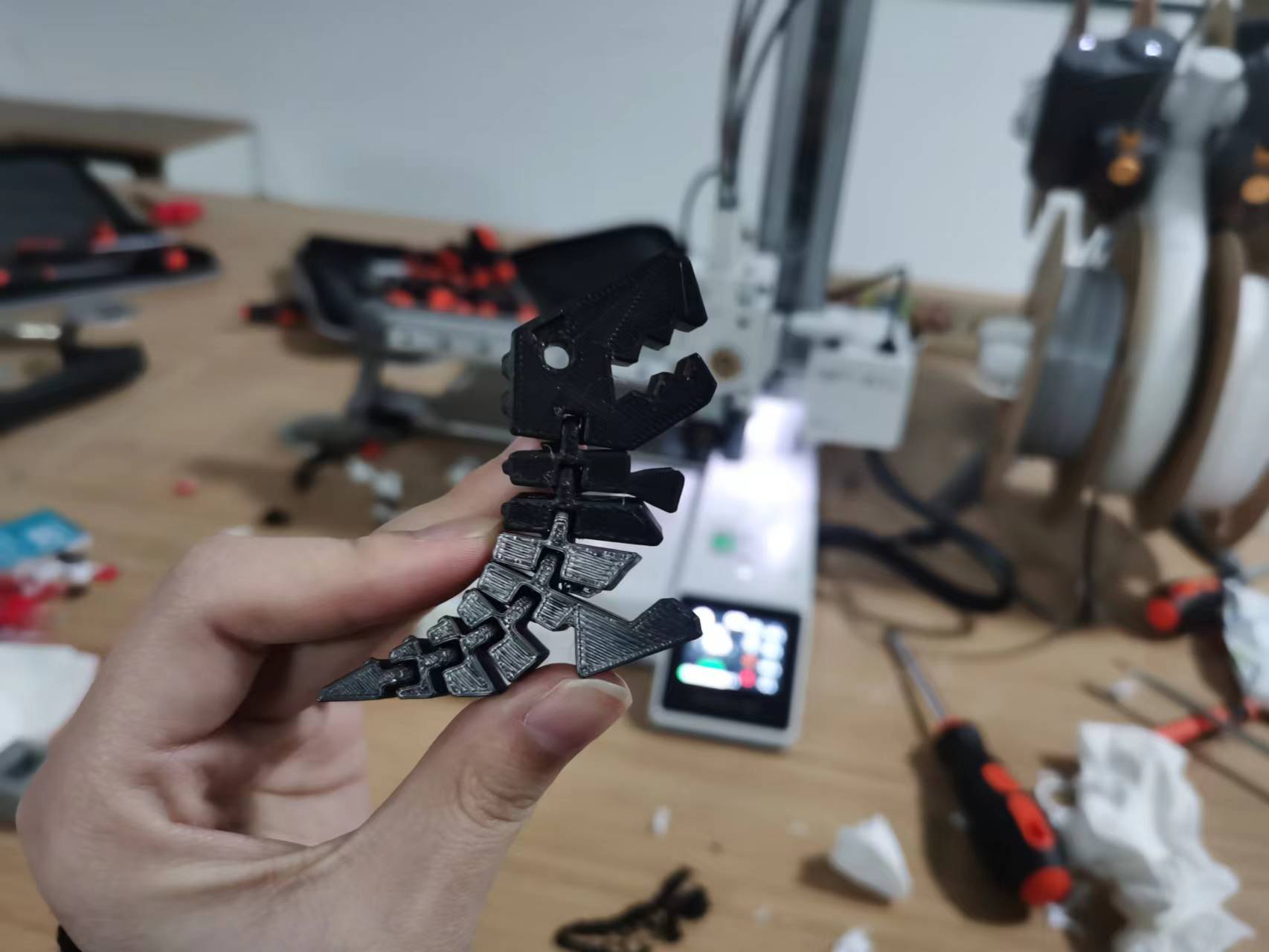
The bottom support can be removed by sanding and removing it. With the support removed, the model is ready for movement.
Step 6: Showcase
Model 1: Conch model related to the big work
Model 2: movable small dinosaur model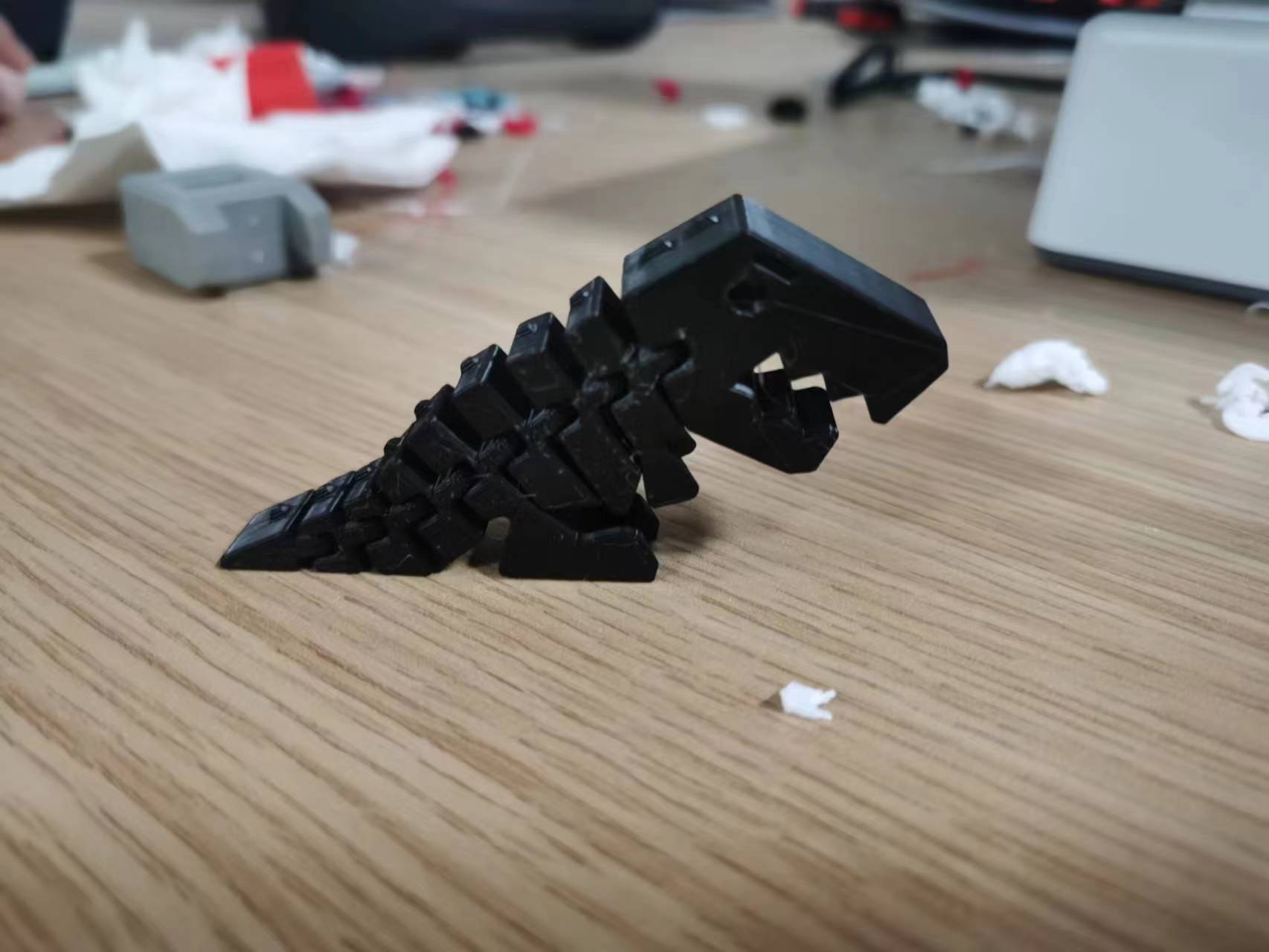
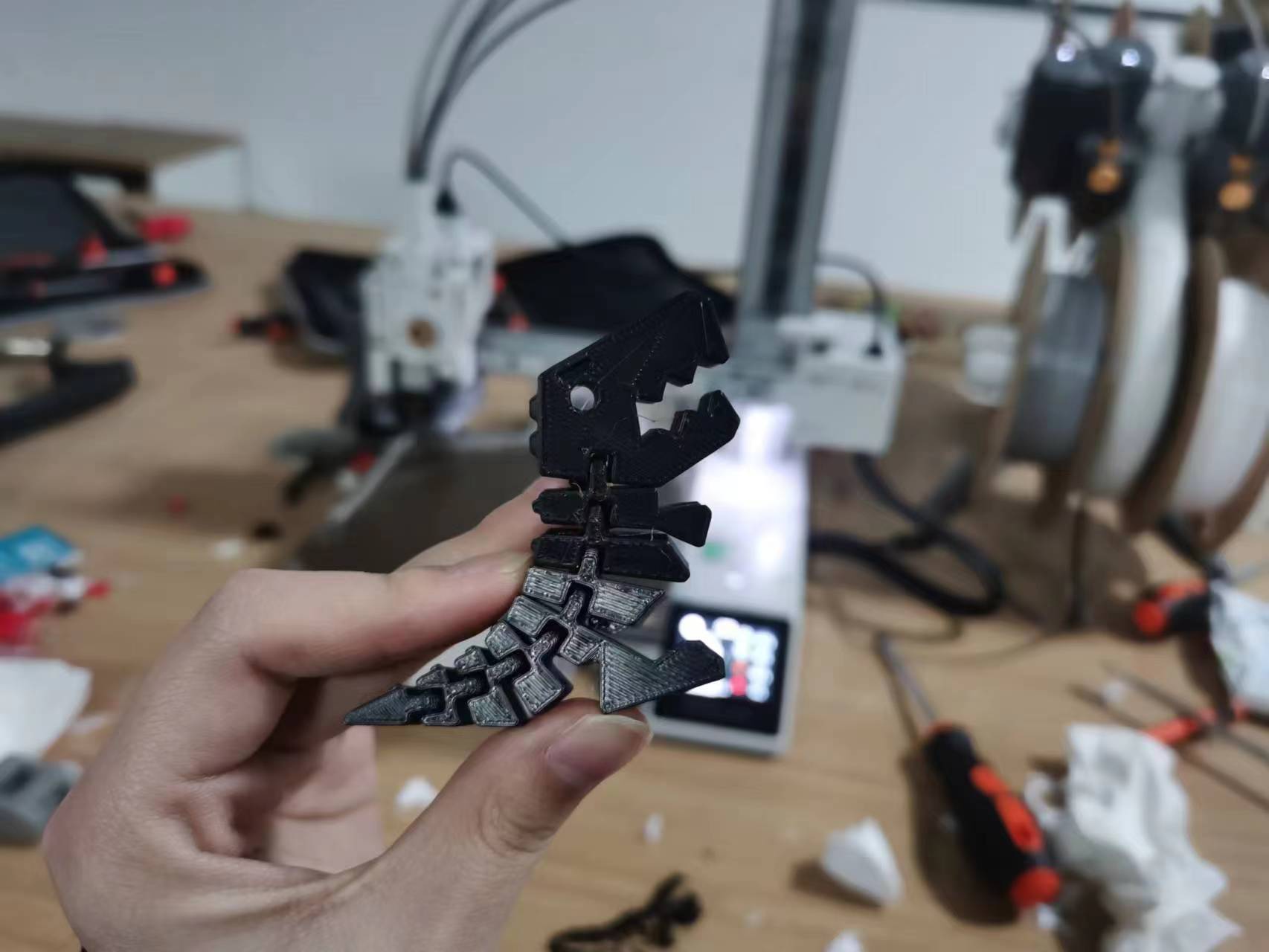

Model 3: assemblable Christmas tree model

Step 7: Find new research or applications
You can keep up with the latest trends and applications in 3D printing by following the relevant forums, communities and official channels on Bambu Studio, as well as GitHub.
Step 8: Try to read the G-code
When using Bambu Studio, it will generate G-code for our model. This G-code is essentially a set of instructions that our 3D printer will follow to create prints. It is important for us to familiarise ourselves with the basics of G-code. Understanding G-code will help us get a handle on how our printer interprets and executes print jobs, and it will be especially useful when we need to troubleshoot or make specific adjustments to our printing process.