Processing(Introduction and Interactive Program)
Processing Introduction
Processing is a programming language and integrated development environment (IDE) for creative coding and visualization. It is designed to allow artists, designers and non-programmers to easily learn to code and create a variety of projects such as graphics, animation and audio applications through visualization and interactivity. The Processing language is based on Java, but is much simpler for beginners to understand.
Characteristics of Processing
Processing is a programming language and integrated development environment (IDE) for creative coding and visualization. Here are some key features:
For artists and designers: Processing is designed to make it easy for non-programmers, especially artists and designers, to learn and use programming. The syntax is relatively simple and easy to understand, making it easier for beginners to get started.
Visualization and interactivity: Processing provides a rich graphics and animation library that enables users to create complex visualizations by writing relatively simple code. Interactivity is also an important feature, and users can interact with their projects in real time through input devices such as mouse and keyboard.
Based on Java: The Processing language is based on the Java programming language, which means that users can take advantage of the power of Java while easing the learning curve by using the simplified syntax of Processing.
Cross-platform: Processing is cross-platform and can run on multiple operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Open Source: Processing is open source, which means that users can access and modify its source code to meet specific needs or contribute to the community.
Basic Processing operations
Processing provides a series of basic operations, so that users can easily draw, interact, and animation operations. Here are some common basic operations in Processing:
- Draw the basic shape:
- point(x, y) : Draws a point at the specified position.
- line(x1, y1, x2, y2) : Draws a straight line.
- rect(x, y, width, height) : Draws a rectangle.
- ellipse(x, y, width, height) : Draws an ellipse.
- Set the color:
- fill(r, g, b) : Set the fill color.
- stroke(r, g, b) : Sets the stroke color.
- background(r, g, b) : sets the background color.
- Text manipulation:
- text(“Hello”, x, y) : Draws text at the specified location.
- textSize(size) : specifies the text size.
- textAlign(LEFT|CENTER|RIGHT) : Sets the text alignment mode.
- Interaction:
- mouseX and mouseY: Obtain the current position of the mouse.
- mousePressed and mouseReleased: detects the mouse press and release.
- keyPressed and keyReleased: Detects keyboard press and release events.
- Animation:
- setup() : Sets initialization parameters, which are executed only once at the beginning of a program.
- draw() : Executes on each frame to draw an animation.
- frameRate(fps) : Sets the frame rate for animation.
- Arrays and loops:
- int[] arr = {1, 2, 3} : Creates an array of integers.
- for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { … } : Loops through groups of numbers.
The following shows the basic operations in the form of code blocks
1 | |
Interesting use of Processing
Beyond these basic operations, processing can be used in many more interesting ways.
Image processing: Methods of importing pictures and processing pictures
1 | |
Sound processing: Method of importing sound
1 | |
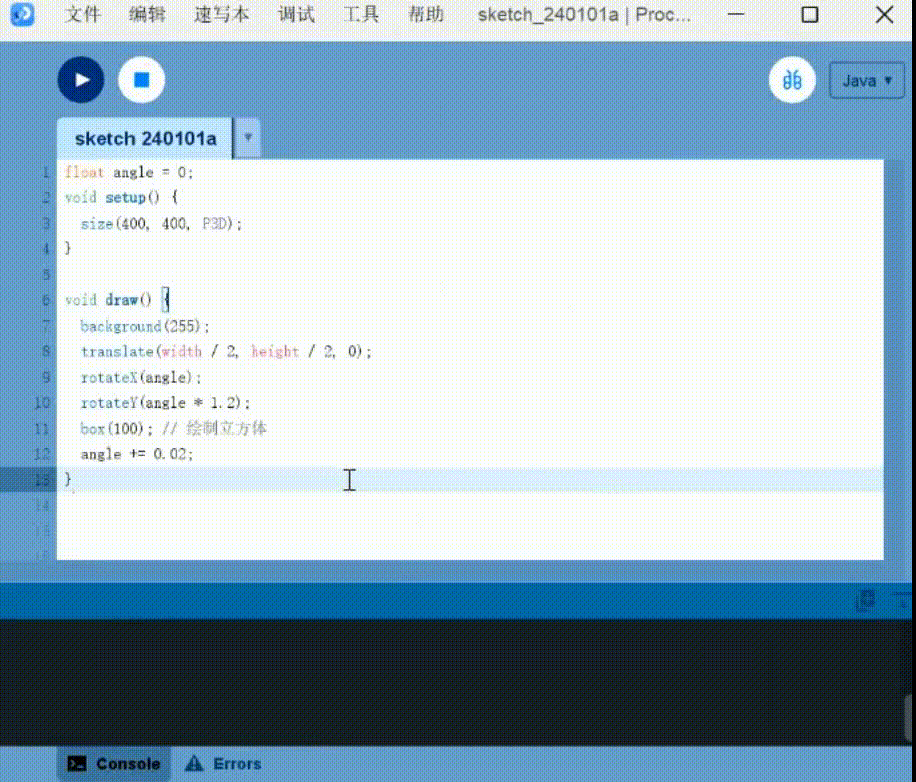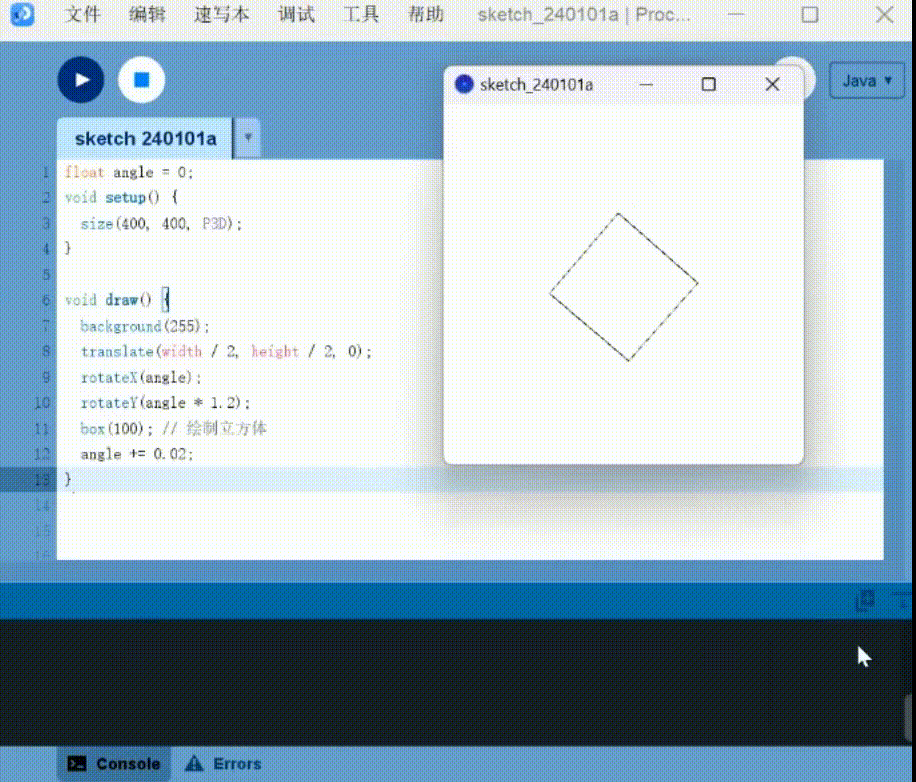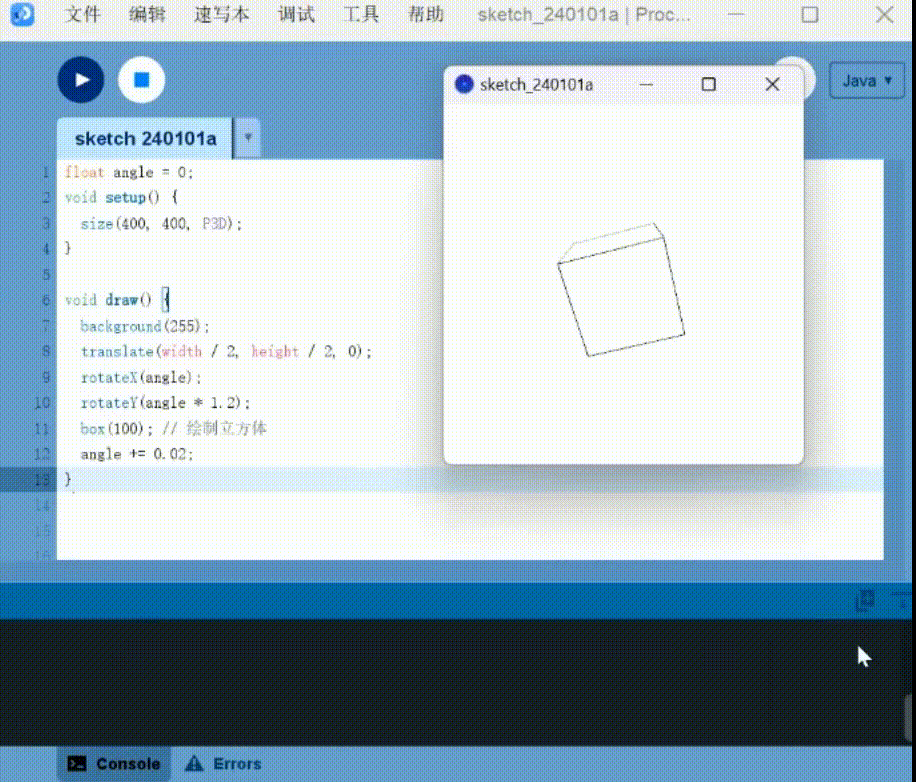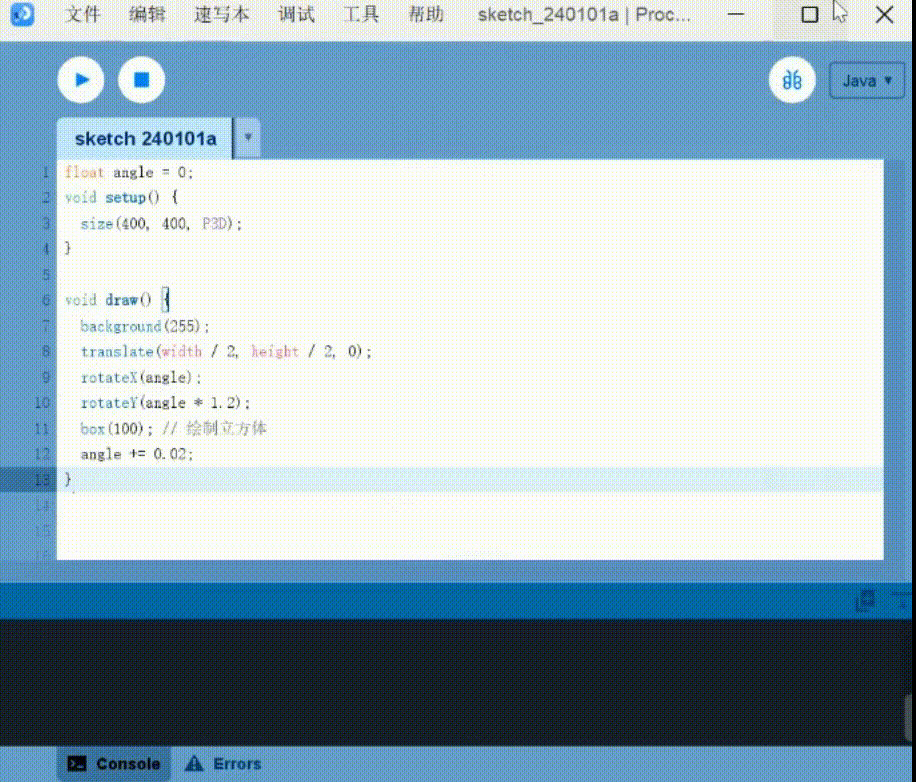
3D drawing: Generate SD cubes that can be moved
1 | |
Similar tools to processing
In addition to processing, there are some other software that can support creative design with processing, such as p5.js, OpenFrameworks, Cinder, TouchDesigner, etc.
p5.js:
p5.js is a JavaScript library designed to enable artists and designers to create interactive graphics and animations by writing simple code. It is a JavaScript version of Processing that supports Web development and runs in the browser.
OpenFrameworks:
OpenFrameworks is an open source C++ framework for creative programming and artistic creation. It offers a wealth of features, including libraries for graphics, image processing, audio, video, and computer vision, and is suitable for multiple platforms.
TouchDesigner
TouchDesigner (abbreviated TD) is a Node Base based visual programming language for real-time interactive multimedia content, developed by Toronto based Derivative. It is used by artists, programmers, creative coders, software designers and performers to create performance, installation and fixed media works.
Operation interface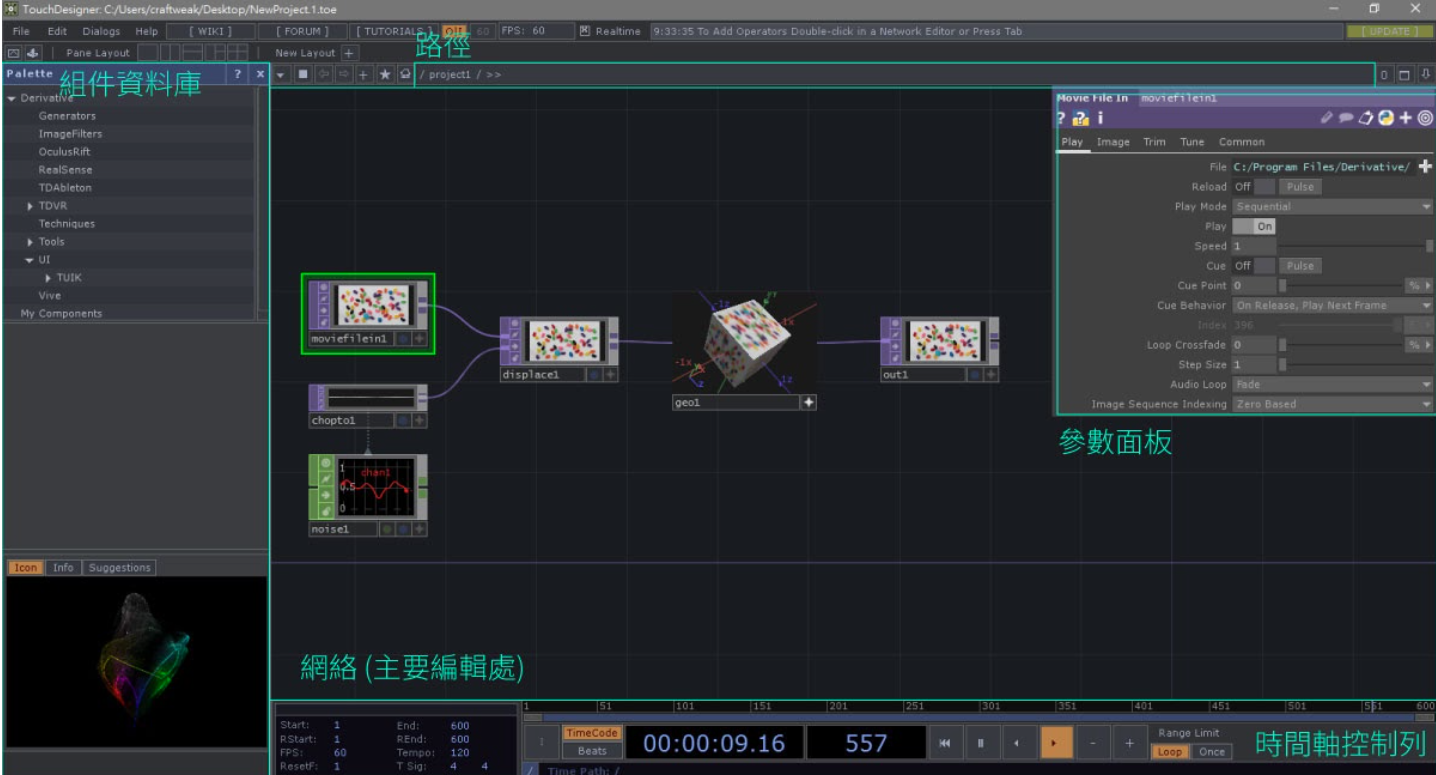
COMPs - Components - Components
Object components (3D objects), panel components (2D UI widgets) and other components. Components can contain other operators.

Compared to other operand families, components (or COMPs) are unique because they contain their own network. To create a new network in your project, use the OP Create menu to create a new component and then select from the COMP signage. Then go into the new component and start building the network. A component network may contain operational units and/or additional subnetworks (add-ons). Subnetworks create network hierarchies that can be navigated (using network paths) and form an overall hierarchy of.toe /.tox files.
TOPs-Texture Operators - texture operands
All 2D image operations.
The texture operand, or TOP, is a fundamental aspect of almost every project. They are 2D texture operands that handle everything from video playback, 3D geometry rendering, composits, hardware image input and output, and are used to process everything that will be output to a monitor, projector, or LED display.
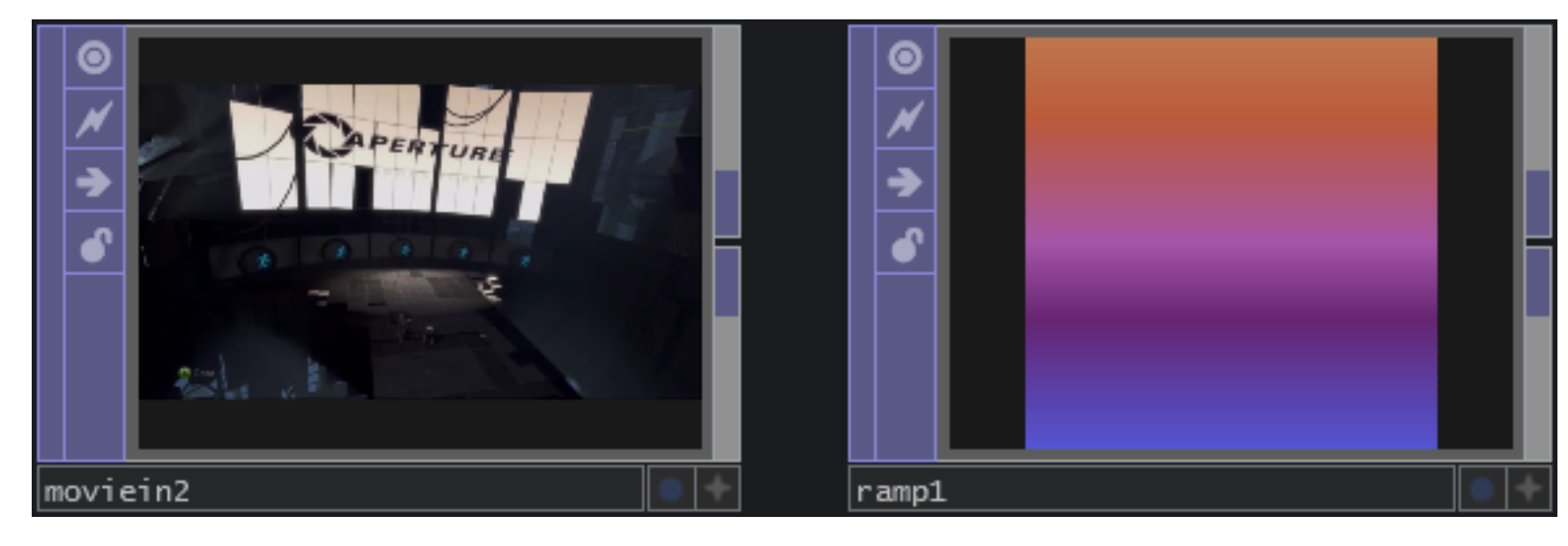
CHOPs - Channel Operators - channel operators
Motion, audio, animation, control signals
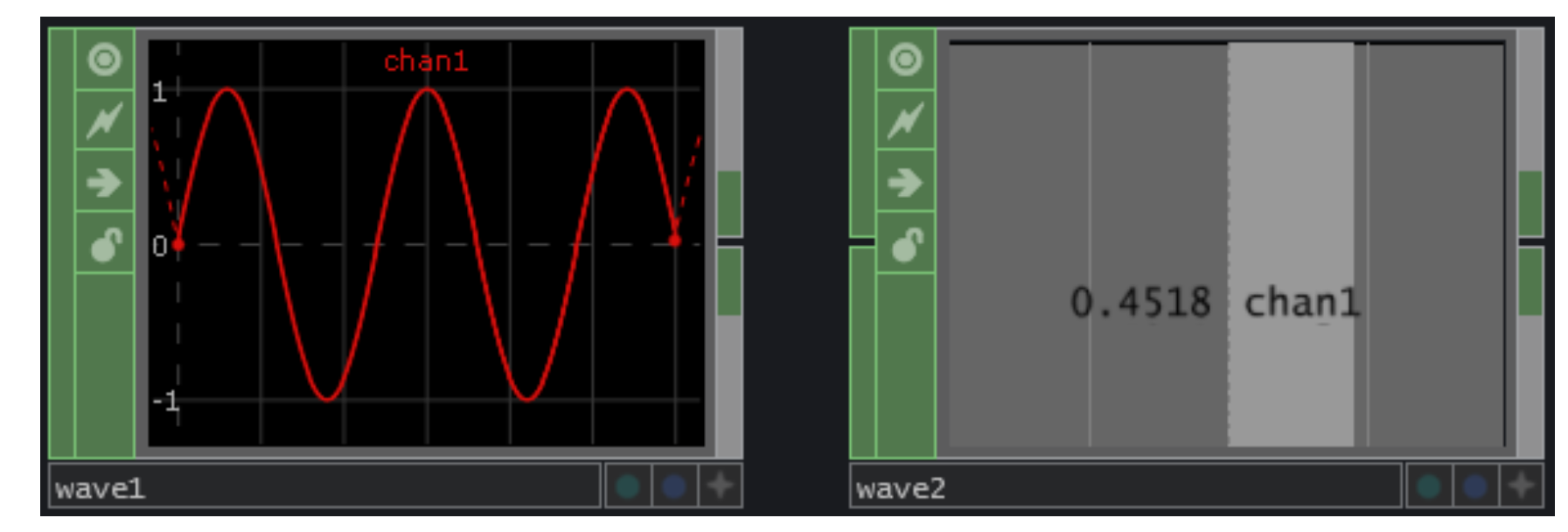
CHOP Series operators handle all channel operations, including Motion data, audio input, keyframe animation, hardware input (from Microsoft Kinect, Leap Motion, Oculus Rift, tablet, keyboard, mouse, etc.), DMX, MIDI, and OSC. These operators handle the input, processing and output of data used to communicate with many types of audiovisual equipment, such as:
- Mixers
- MIDI controllers
- synthesizer
- DMX lighting fixtures
- Microsoft Kinect camera
- Computers running TouchDesigner
- sound
- Other audio-video applications such as Max/MSP, Ableton Live, Resolume Arena
- Pattern Expansion
- SOP-Surface Operators - Surface Operators
SOP-Surface Operators - Surface Operators
3D points, polygons and other 3D “primitives”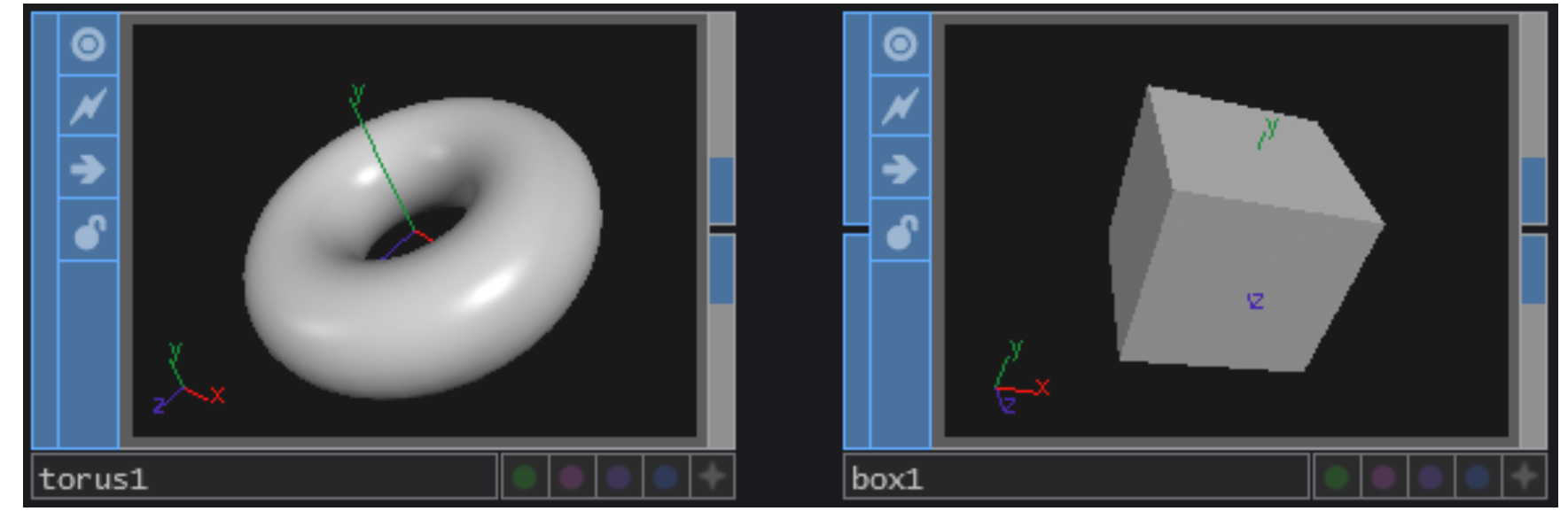
SOP is an operator that can generate, import, modify and combine 3D surfaces (also known as geometry). The surface types are polygons, curves, NURBS surfaces, metaball and particles.
DAT-Data Operators - Data operation elements
ASCII text is organized as plain text, script, XML, or by cell table.
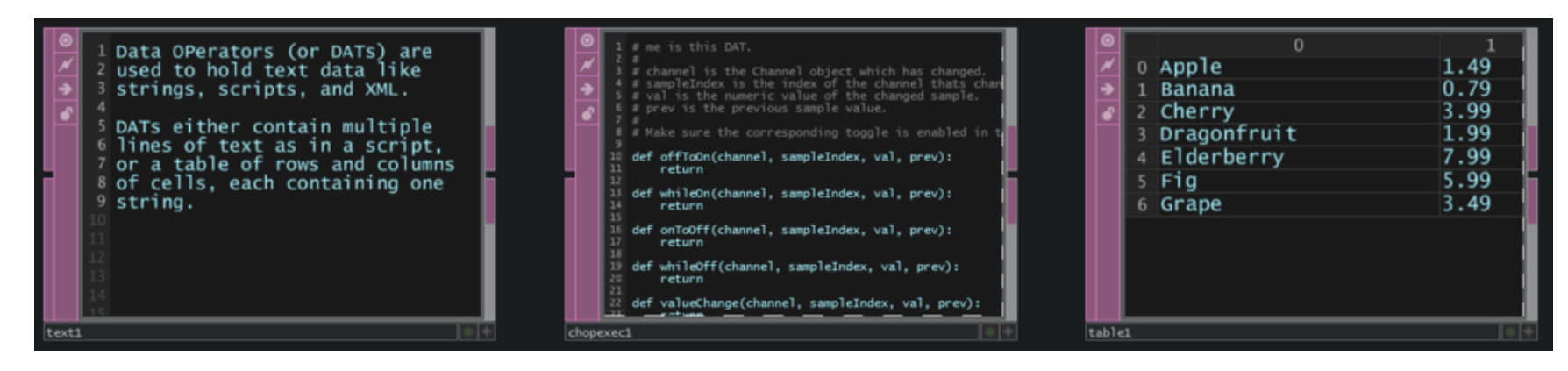
Data operators (DAT) perform operations on data. They can edit, parse, create, send and receive data in various forms. These forms of data can include text strings, tables, Python scripts, XML, JSON, MIDI, serial, OSC, and so on.
The logic system relies heavily on the use of DAT and Python scripts. The ability to parse tables full of information and metadata, monitor other operators and their states, perform complex tasks based on incoming messages from other systems, etc., makes it possible to create fairly complex systems in TouchDesigner.
MATs-Material Operators - Material Operators
Materials and colourers.
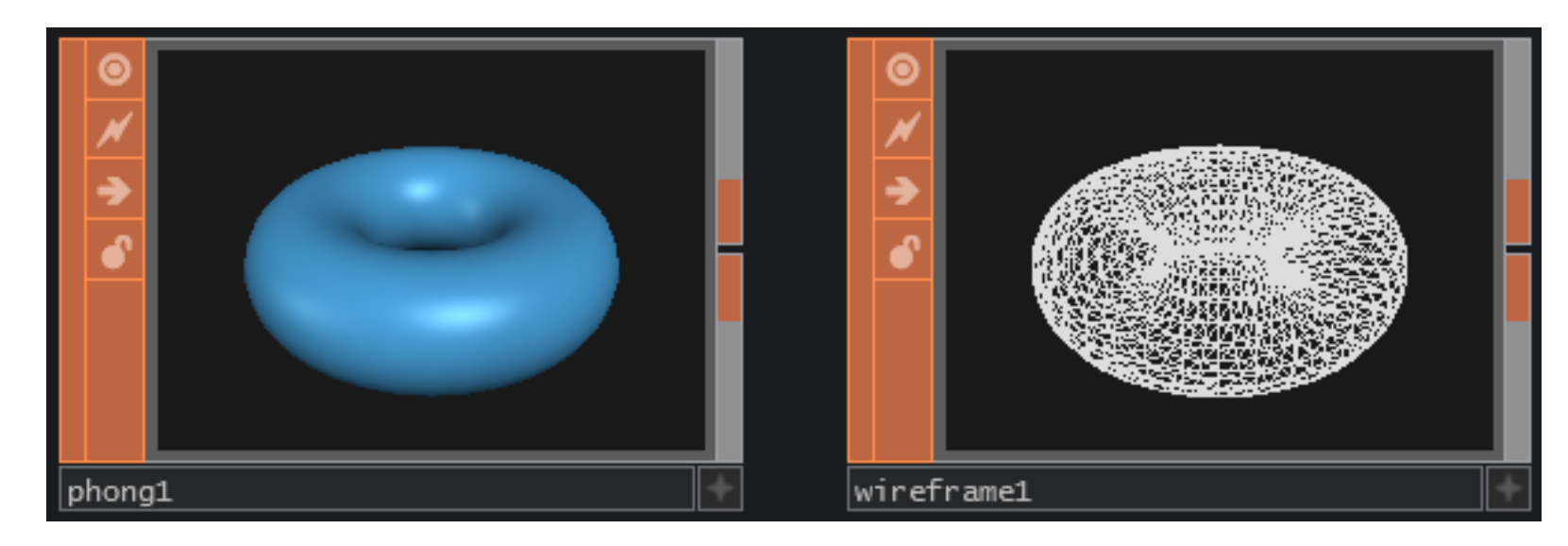
Material Operator (MAT) is used to create materials for geometry. You can apply them to geometry using the Material parameter on the Display page or any Object component.
The Phong MAT and GLSL MAT are designed to create more advanced shaders using TOPS and GLSL programs (pixel and vertex shaders) as inputs.
The most commonly used MAT is the Phong MAT
Parameter (Parameter)
Parameters in TouchDesigner exist only in operators (OP or “nodes”). Parameters include:
- numbers Indicates integers and floating point numbers
- number pairs Pairs of numbers, triples or quadruples (e.g. width and height, XYZ position, RGBA color)
- on-off flags Indicates the switch flag
- menus directory
- text strings Strings
- Paths to other nodes in the TouchDesigner network
- Button for initializing the action (uncommon)
Links between parameters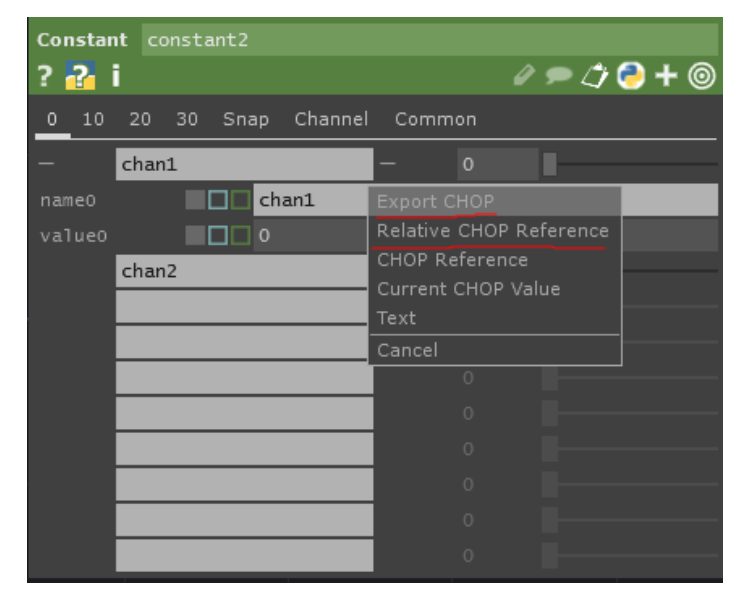
Export CHOP is a direct output, used if the value does not need to be adjusted
The Relative CHOP Reference is an expression with writable syntax, mainly Python syntax
Processing interaction
In Processing, you can use a mouse and keyboard to interact. Here is some sample code for basic mouse and keyboard interaction:
Mouse interaction:
Detecting mouse position:
1 | |
Detecting mouse buttons:
1 | |
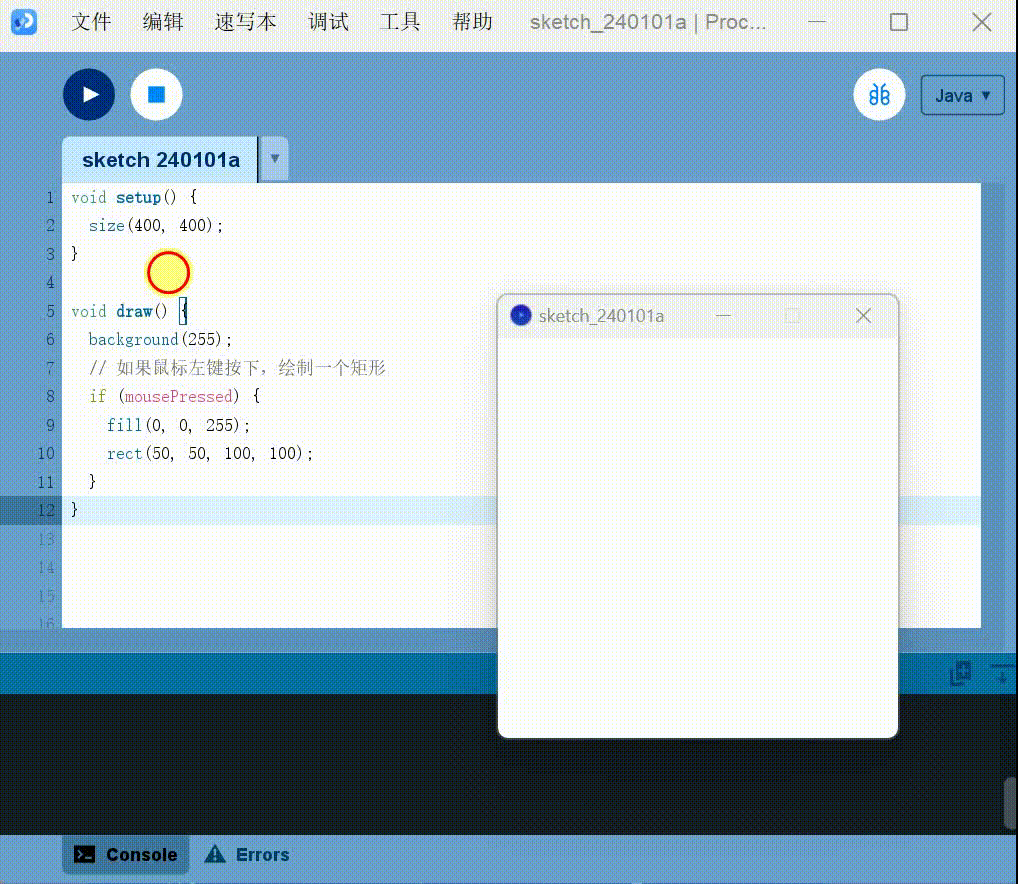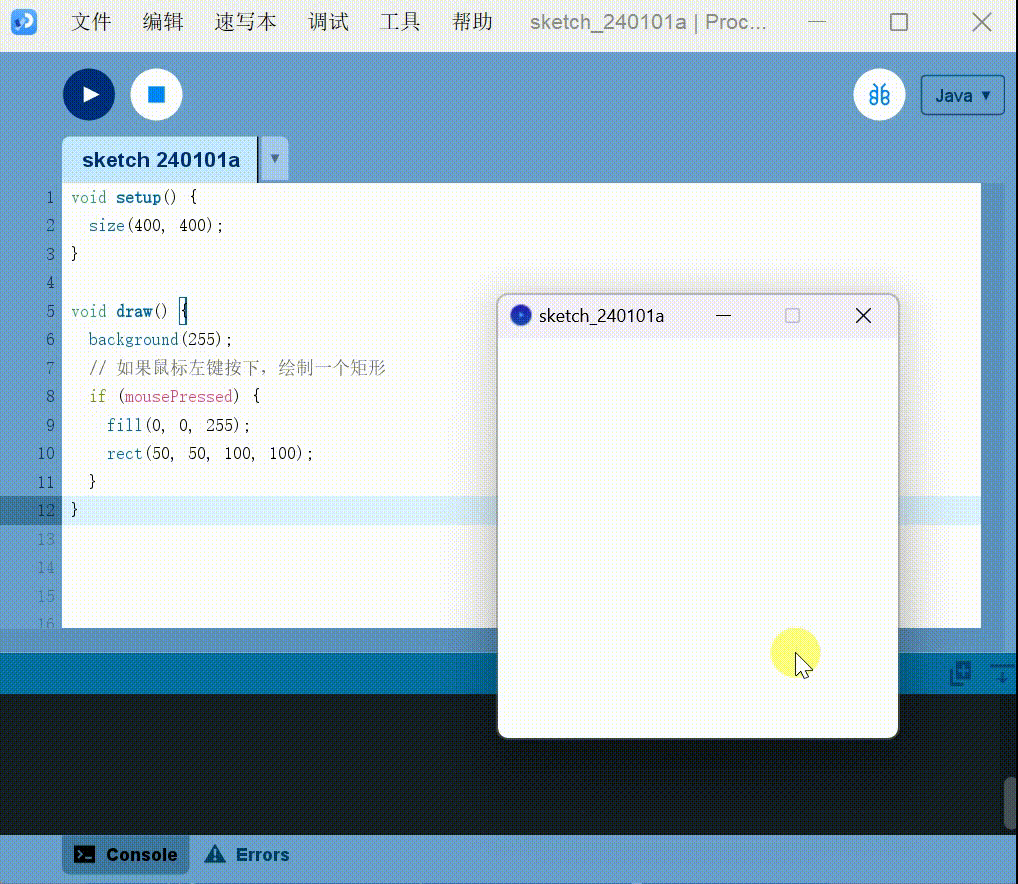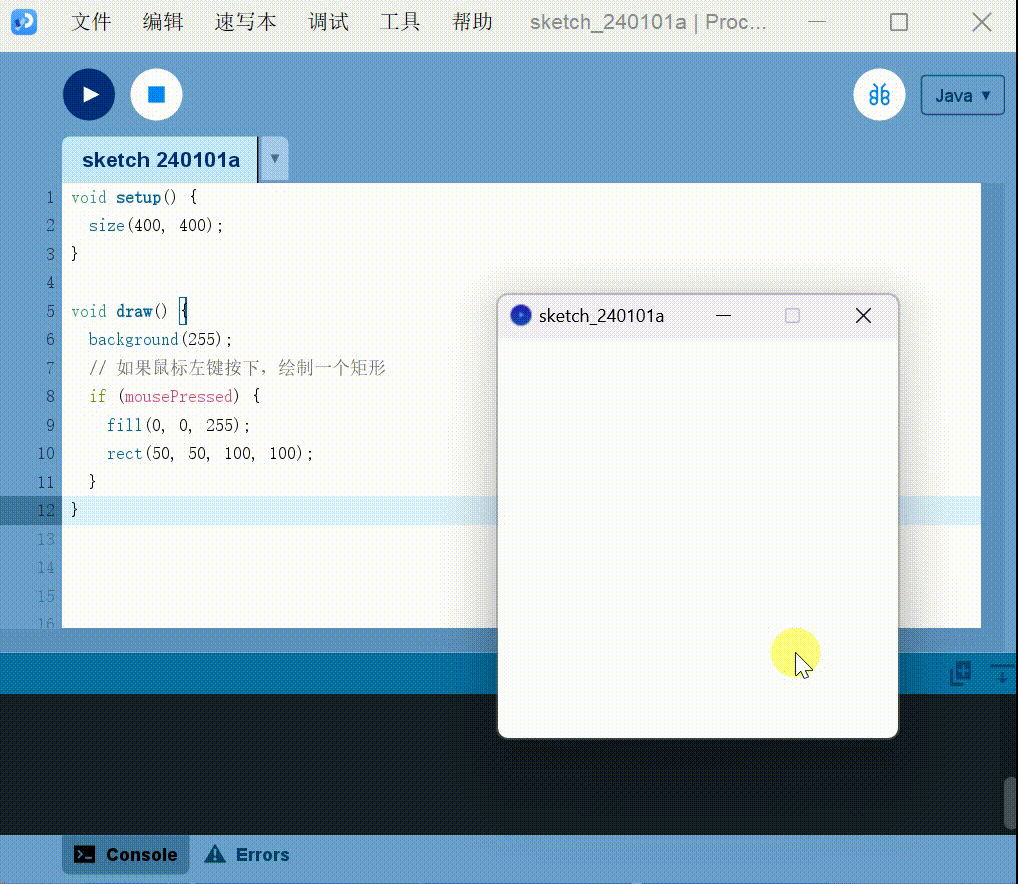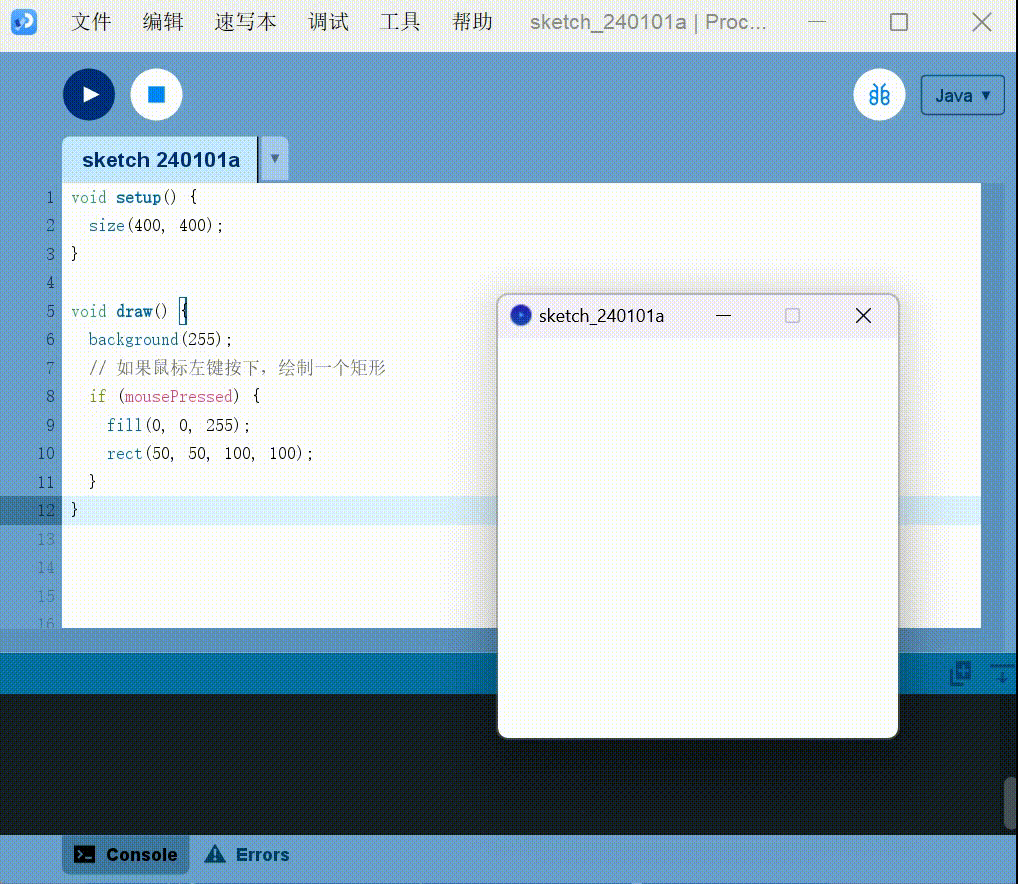
Keyboard interaction:
Detect key:
1 | |
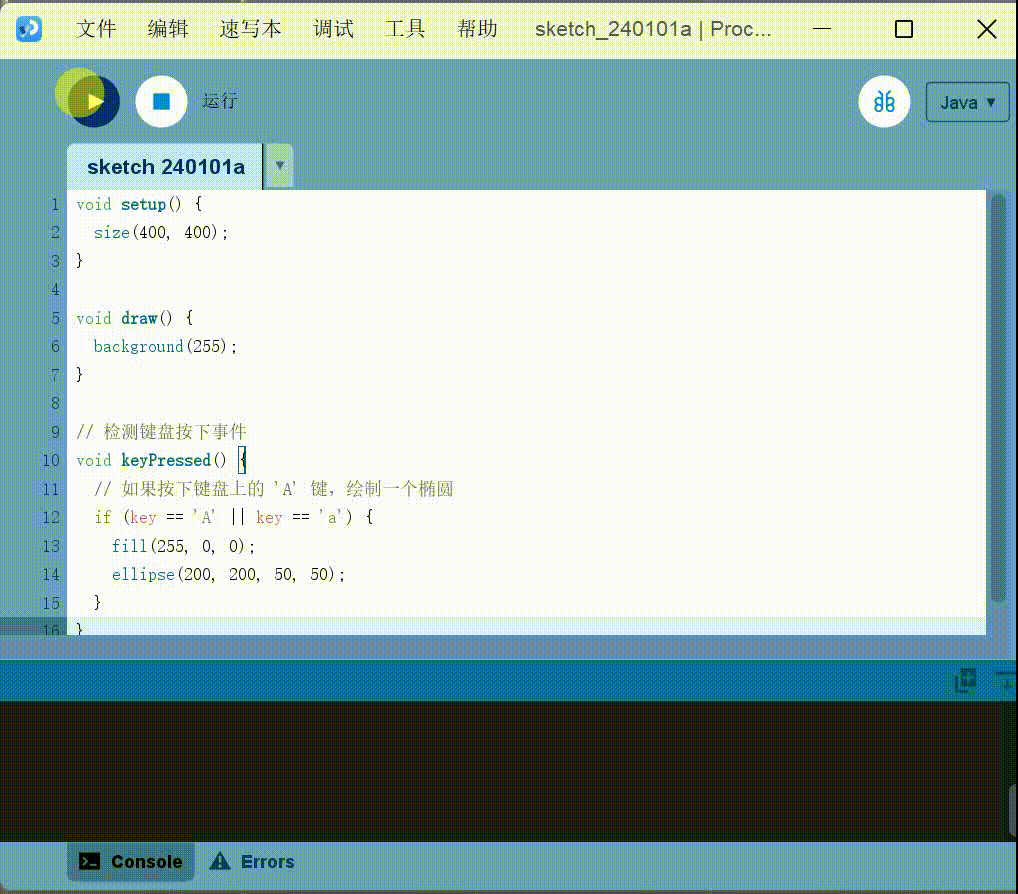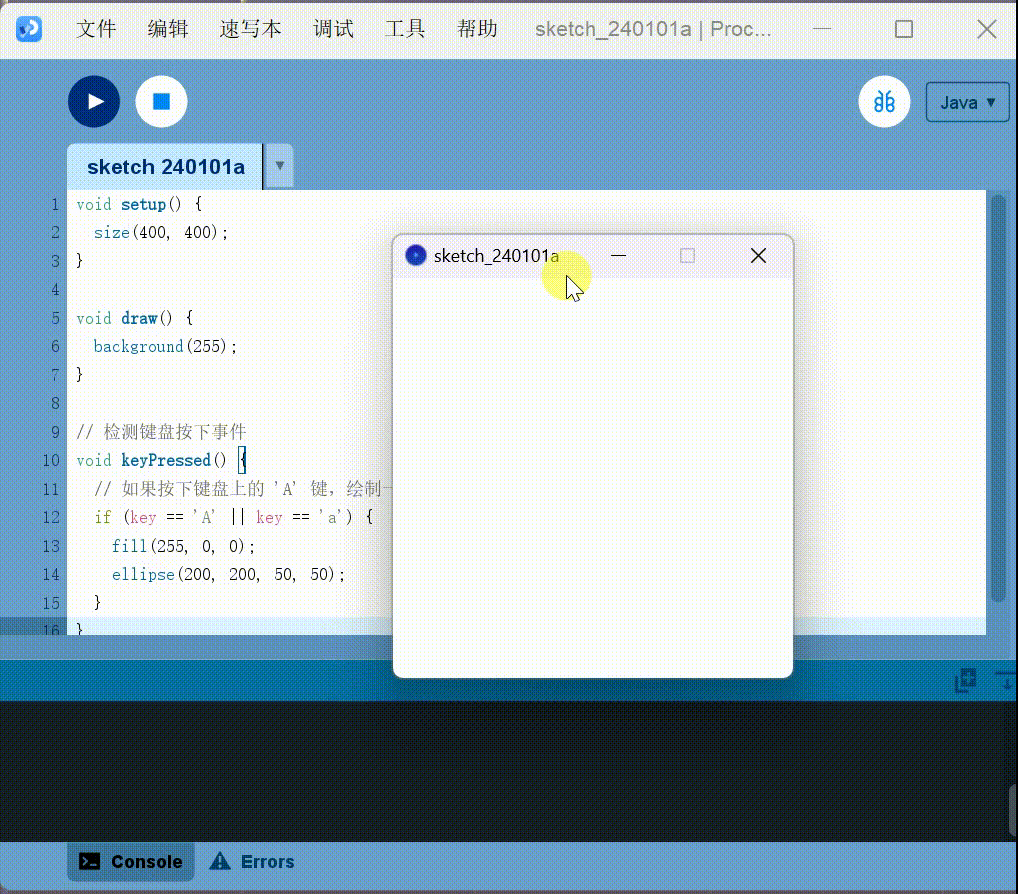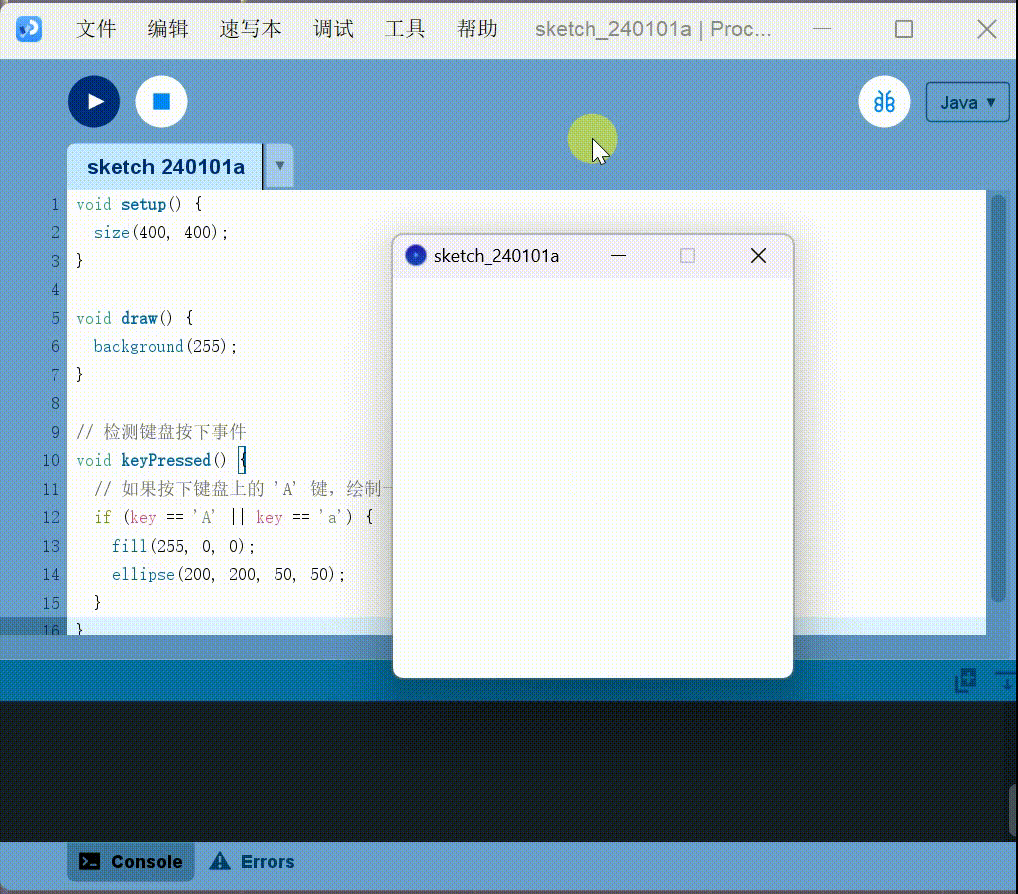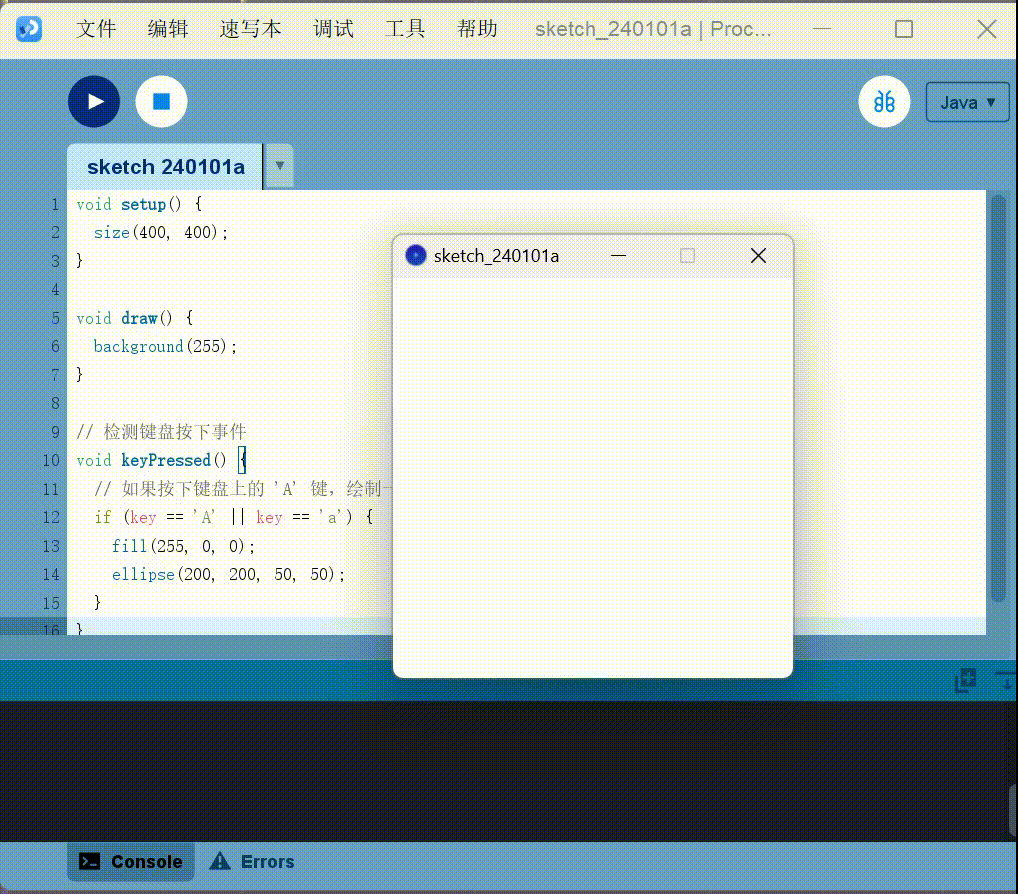
Get keyboard keys:
1 | |
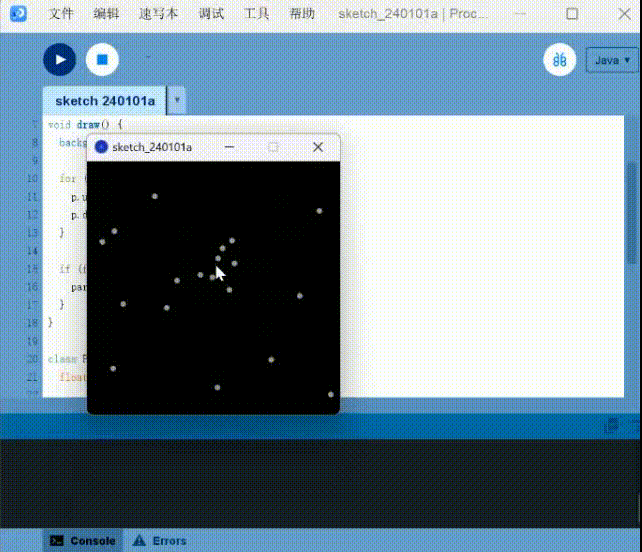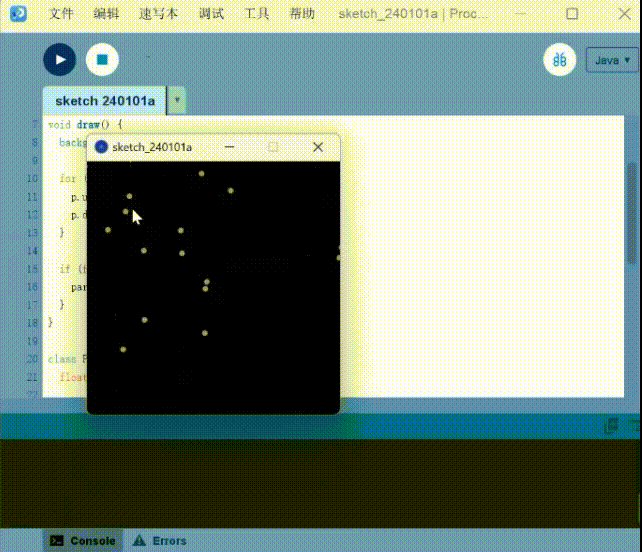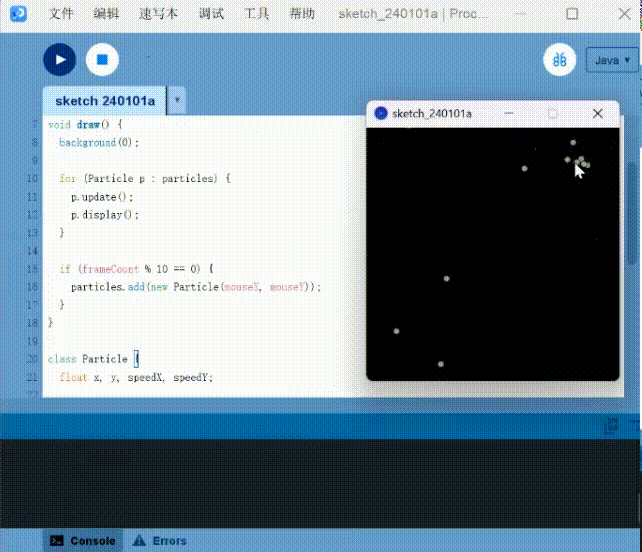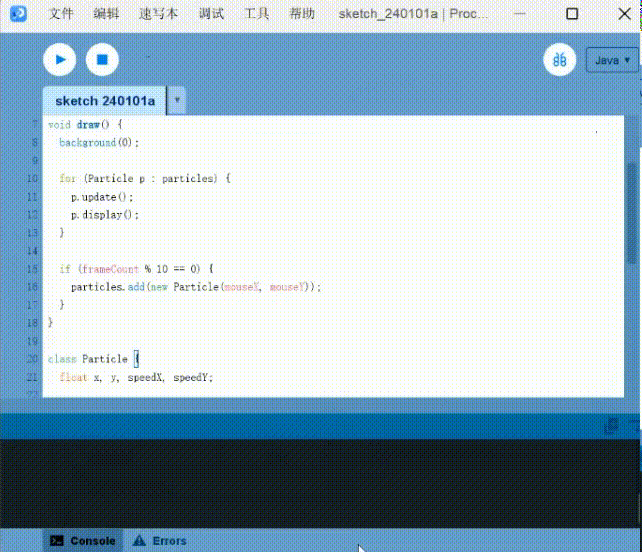
Here is a small example of using a mouse to produce a quantum effect.
Particle systems: Use the mouse to generate quantum interactions
1 | |